Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2014; 20(29): 10071-10081
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10071
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10071
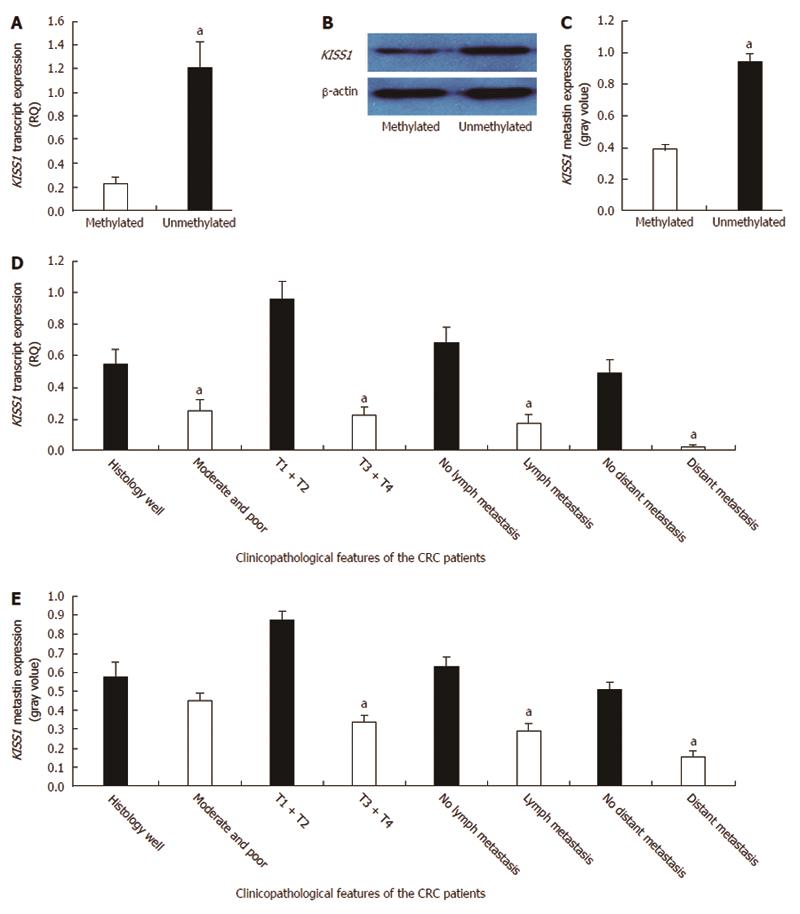
Figure 2 Correlations between KISS1 expression and methylation and clinicopathological factors in colorectal cancer patients.
A: KISS1 transcript expression in 126 colorectal cancer (CRC) patients was determined by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The data are presented as the mean ± SD. KISS1 transcript expression was significantly lower in the methylated KISS1 group than in the unmethylated KISS1 group (aP < 0.05 vs the methylated KISS1 group); B: KISS1/metastin protein levels in CRC tissues of the indicated genotypes were determined by Western blot. The same membranes were subsequently probed with an anti-β-actin antibody as a loading control; C: The KISS1/metastin protein expression levels are presented as the mean ± SEM. aP < 0.05 vs the methylated KISS1 group; D: The analysis of the relationship between KISS1 transcript expression and patient clinicopathological factors revealed a negative correlation with tumor differentiation, depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis (aP < 0.05); E: Metastin expression was also negatively correlated with the depth of invasion, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis (aP < 0.05).
-
Citation: Chen SQ, Chen ZH, Lin SY, Dai QB, Fu LX, Chen RQ.
KISS1 methylation and expression as predictors of disease progression in colorectal cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(29): 10071-10081 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i29/10071.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10071