Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2014; 20(29): 10038-10049
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10038
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10038
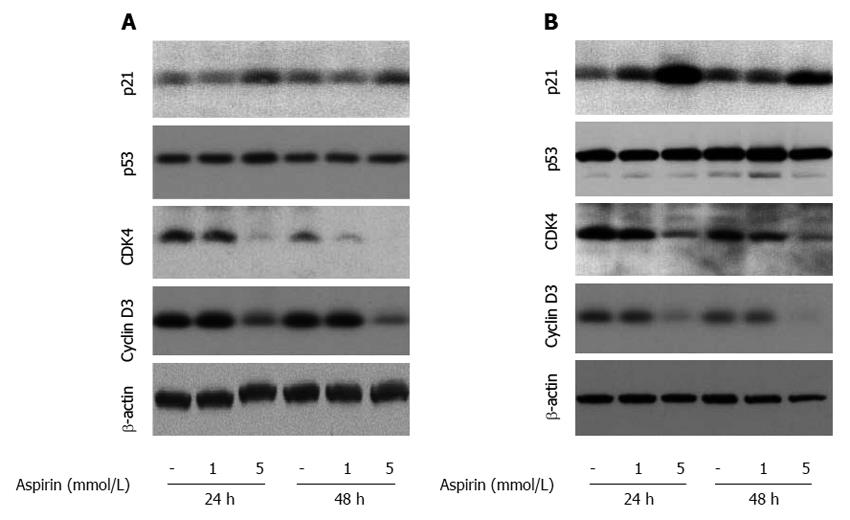
Figure 9 The effect of aspirin on proteins involved in cell cycle progression in neuroendocrine BON1 and NCI-H727 tumor cells.
Human pancreatic neuroendocrine BON1 (A) and human bronchopulmonary NCI-H727 (B) cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of aspirin for 24 and 48 h. The expression of p21, CDK4, p53, cyclin D3 and a β-actin loading control was subsequently evaluated by Western blot analysis. A representative blot from 3 independently performed experiments is shown.
- Citation: Spampatti M, Vlotides G, Spöttl G, Maurer J, Göke B, Auernhammer CJ. Aspirin inhibits cell viability and mTOR downstream signaling in gastroenteropancreatic and bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine tumor cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(29): 10038-10049
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i29/10038.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10038