Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2014; 20(28): 9506-9512
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9506
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9506
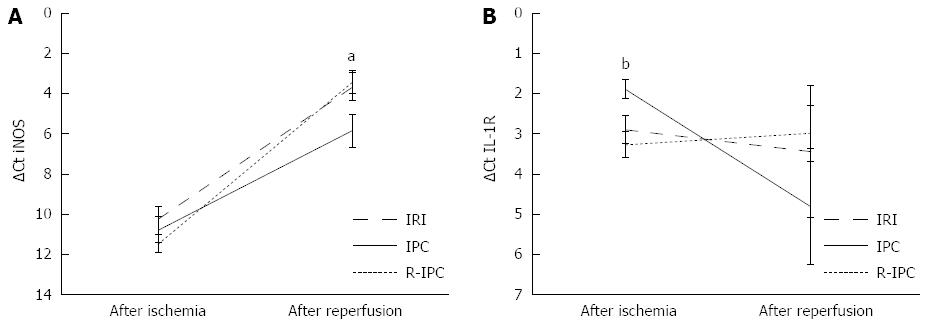
Figure 2 Inducible nitric oxide synthase or interleukin-1R mRNA in liver tissue (mean ± SE) in rats previously subjected to 60 min of ischemia/reperfusion injury after ischemic preconditioning or remote ischemic preconditioning.
A: iNOS transcription. The iNOS transcription was significantly increased in the R-IPC group (n = 8) after 4 h of reperfusion compared with the IPC group (n = 8), aP < 0.05 vs IPC group; B: IL-1R transcription. The IL-1R transcription decreased in the IPC group during reperfusion (P = 0.027) but did not change in the R-IPC group. The transcription after ischemia was higher in the IPC group than in the R-IPC group; bP < 0.01, IPC group vs R-IPC group. iNOS: Inducible nitric oxide synthase; IL-1R: Interleukin-1R; IPC: Ischemic preconditioning; R-IPC: Remote ischemic preconditioning.
- Citation: Björnsson B, Winbladh A, Bojmar L, Sundqvist T, Gullstrand P, Sandström P. Conventional, but not remote ischemic preconditioning, reduces iNOS transcription in liver ischemia/reperfusion. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(28): 9506-9512
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i28/9506.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9506