Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2014; 20(28): 9506-9512
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9506
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9506
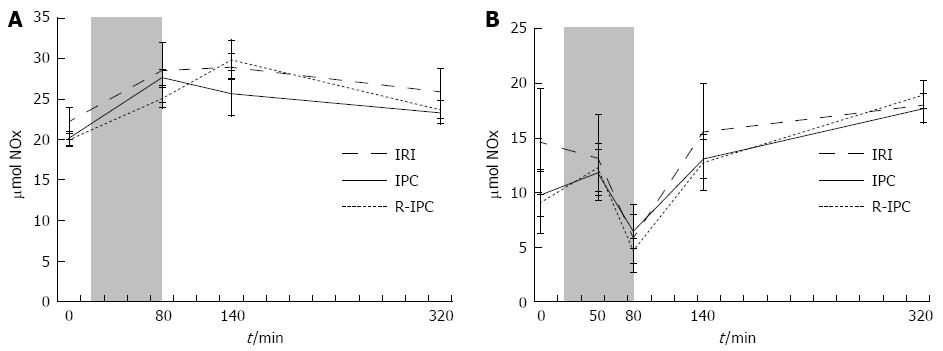
Figure 1 Nitrite and nitrate in serum or in microdialysis (mean ± SE) in rats subjected to 60 min of segmental (left lateral lobe) ischemia (shaded area) of the liver and 4 h of reperfusion after conventional or remote ischemic preconditioning.
A: Nitrite and Nitrate in serum. Initially, a significant rise was observed during the ischemia followed by a significant fall during the reperfusion in both the IPC and the R-IPC groups. For the IPC group, the fall started immediately after ischemia, but in the R-IPC group, a rise was observed during the first 60 min of reperfusion; B: Nitrite and Nitrate in microdialysis. In both the IPC and R-IPC groups, the NOx levels dropped significantly during ischemia in the ischemic lobes, but during reperfusion there was an upward trending movement. In the control lobes, no fall was observed during ischemia. IPC: Ischemic preconditioning; R-IPC: Remote ischemic preconditioning; NOx: Nitrite and nitrate; IRI: Ischemia/reperfusion injury.
- Citation: Björnsson B, Winbladh A, Bojmar L, Sundqvist T, Gullstrand P, Sandström P. Conventional, but not remote ischemic preconditioning, reduces iNOS transcription in liver ischemia/reperfusion. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(28): 9506-9512
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i28/9506.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9506