Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2014; 20(28): 9486-9496
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9486
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9486
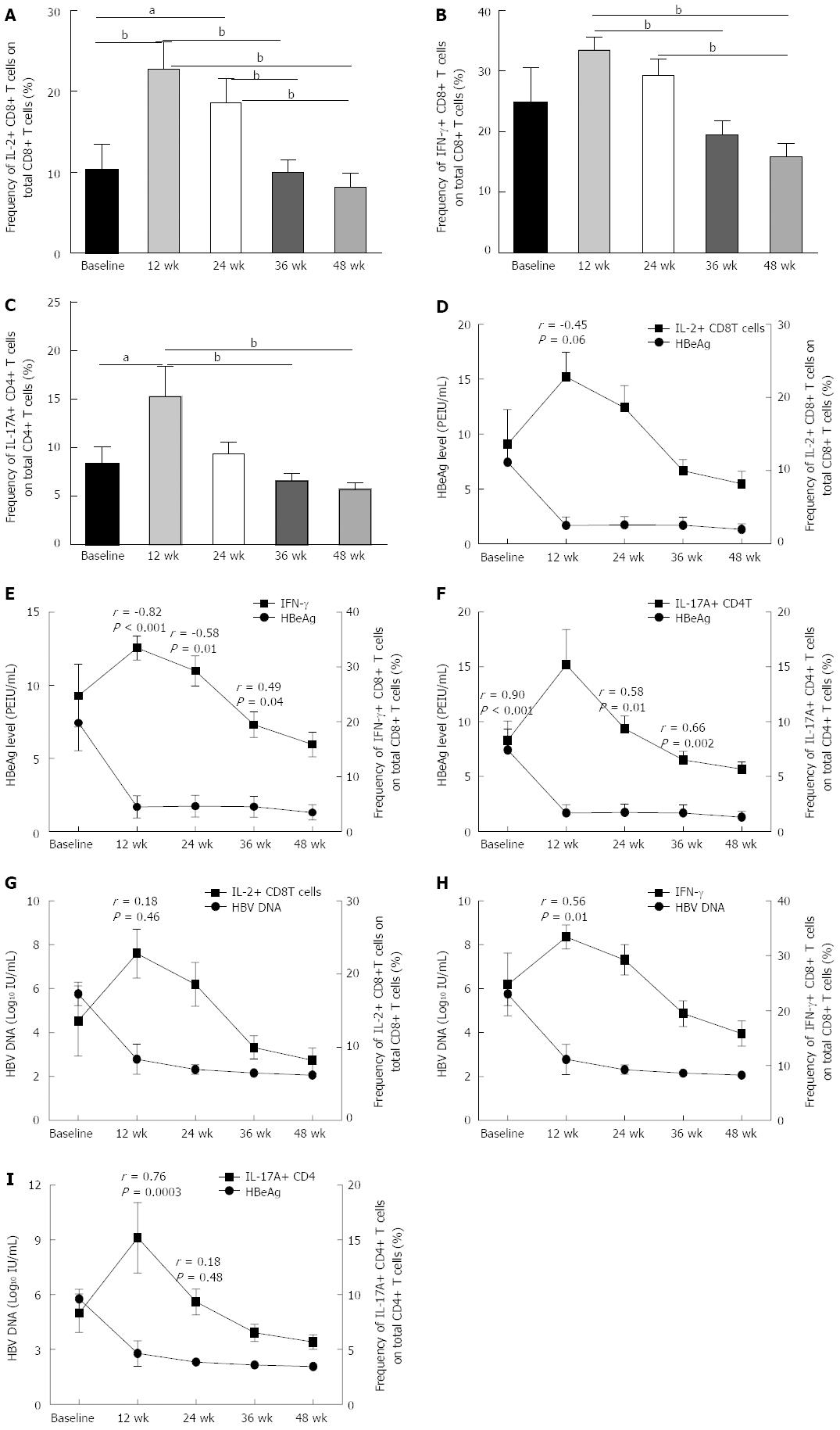
Figure 4 Correlations between viral infection parameters and the frequency of pro-inflammatory cytokine-secreting T cells in chronic hepatitis B patients on nucleoside analogue therapy.
The frequency of pro-inflammatory cytokine-secreting T cells increased significantly at treatment weeks 12 and 24. A: Frequency of interleukin-2 positive CD8 T cells (IL-2+ CD8 T); B: Frequency of interferon-gamma positive CD8 T cells (IFN-γ+ CD8 T); C: Frequency of interleukin-17A positive CD4 T cells (IL-17A+ CD4 T); D: Correlation between the hepatitis B envelope antigen (HBeAg) level and the frequency of IL-2+ CD8 T cells; E: Correlation between the HBeAg level and the frequency of IFN-γ+ CD8 T cells; F: Correlation between the HBeAg level and the frequency of IL-17A+ CD4 T cells; G: Correlation between the HBV DNA level and the frequency of IL-2+ CD8 T cells; H: Correlation between the HBV DNA level and the frequency of IFN-γ+CD8 T cells; I: Correlation between the HBV DNA level and the frequency of IL-17A+ CD4 T cells. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Li CZ, Hu JJ, Xue JY, Yin W, Liu YY, Fan WH, Xu H, Liang XS. Viral infection parameters not nucleoside analogue itself correlates with host immunity in nucleoside analogue therapy for chronic hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(28): 9486-9496
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i28/9486.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9486