Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2014; 20(27): 9038-9049
Published online Jul 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9038
Published online Jul 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9038
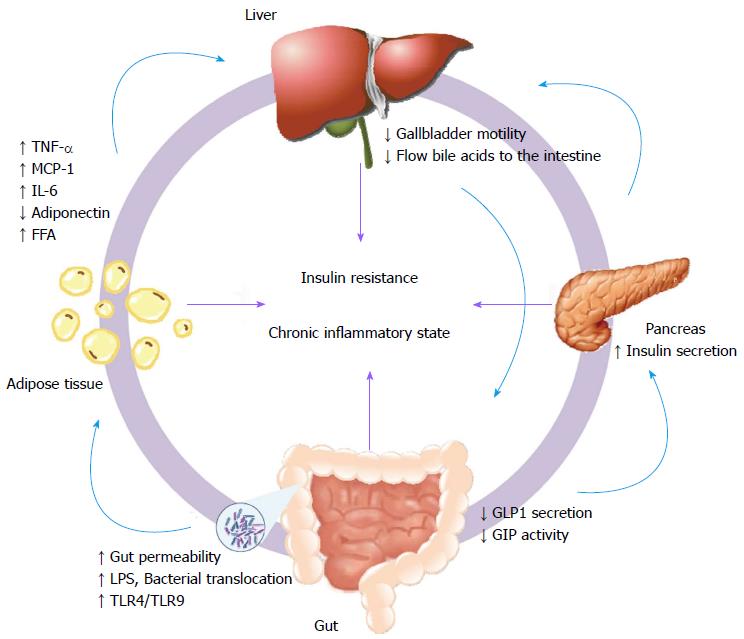
Figure 2 Extrahepatic factors involved in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
The affected organs and their response are represented in a dynamic circle; in the center are indicated the main factors that contribute to the initiation/perpetuation of the hepatic injury (insulin resistance and chronic inflammatory state). The light blue arrows represent the organ-specific effects of each response. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; MCP-1: Monocyte chemotactic protein 1; IL-6: Interleukin-6; FFA: Free fatty acids; LPS: Lipopolysaccharides; TLR: Toll-like receptor; GIP: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide; GLP: Glucagon-like-peptide.
- Citation: Rosso N, Chavez-Tapia NC, Tiribelli C, Bellentani S. Translational approaches: From fatty liver to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(27): 9038-9049
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i27/9038.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.9038