Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2014; 20(27): 8910-8920
Published online Jul 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8910
Published online Jul 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8910
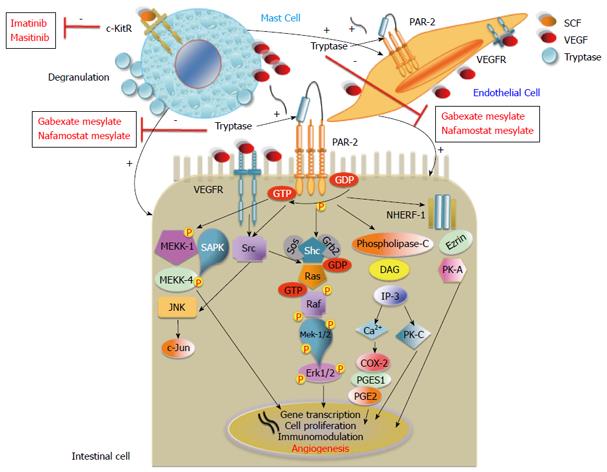
Figure 2 In both intestinal and endothelial cells, the tryptase/proteinase-activated receptor-2 and vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular endothelial growth factor receptor axes, induced by mast cells, lead to tumor angiogenesis and intestinal cell growth.
Note that targeting mast cells with molecular agents (c-KitR tyrosine kinase and tryptase inhibitors) could prevent angiogenesis-mediated colorectal cancer progression. c-KitR: c-Kit receptor; PAR-2: Proteinase-activated receptor-2; VEGFR: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor; SCF: Stem cell factor: VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; NHERF-1: Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor-1; MEKK-1: Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-related kinase-1; MEKK-4: Mitogen-activated protein kinase/ extracellular signal-related kinase-4; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; c-Jun: Jun proto-oncogene; SAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase-9; GEF: Rho/rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor; Rho: Rhodopsin transcription termination factor; SOS: Son of sevenless protein; Grb2: Growth factor receptor-bound protein 2; Shc: Shc transforming protein kinase; Ras: Ras protein kinase; Raf: Raf protein kinase; Mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-related kinase-1/2; Erk: Elk-related tyrosine kinase; DAG: Diacylglycerol; IP-3: Inositol triphosphate; PK-C: Protein kinase-C; COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; PGES-1: Prostaglandin E synthase-1; PK-A: Protein kinase-A.
- Citation: Marech I, Ammendola M, Gadaleta C, Zizzo N, Oakley C, Gadaleta CD, Ranieri G. Possible biological and translational significance of mast cells density in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(27): 8910-8920
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i27/8910.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8910