Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2014; 20(27): 8751-8763
Published online Jul 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8751
Published online Jul 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8751
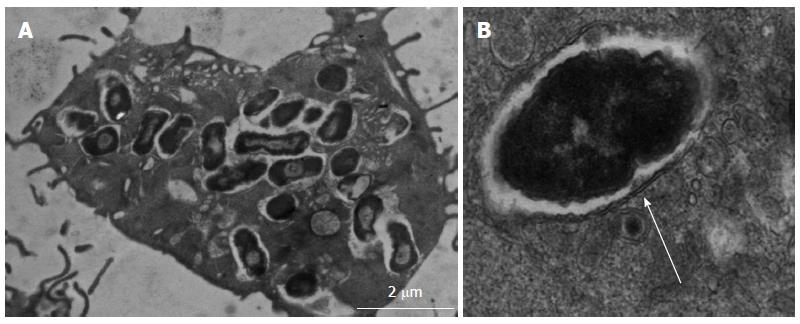
Figure 4 Transmission electron micrograph of adherent, invasive Escherichia coli within macrophages1.
A: Crohn’s disease colonic mucosa-associated isolate HM605 surviving and replicating within vesicles of J774-A1 murine macrophages; B: Double membrane around intra-macrophage vesicle indicates bacteria are contained within phagolysosomes (arrow). 1Images courtesy of Dr. Carol L Roberts (University of Liverpool, United Kingdom).
-
Citation: Tawfik A, Flanagan PK, Campbell BJ.
Escherichia coli -host macrophage interactions in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(27): 8751-8763 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i27/8751.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8751