Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2014; 20(27): 8751-8763
Published online Jul 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8751
Published online Jul 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8751
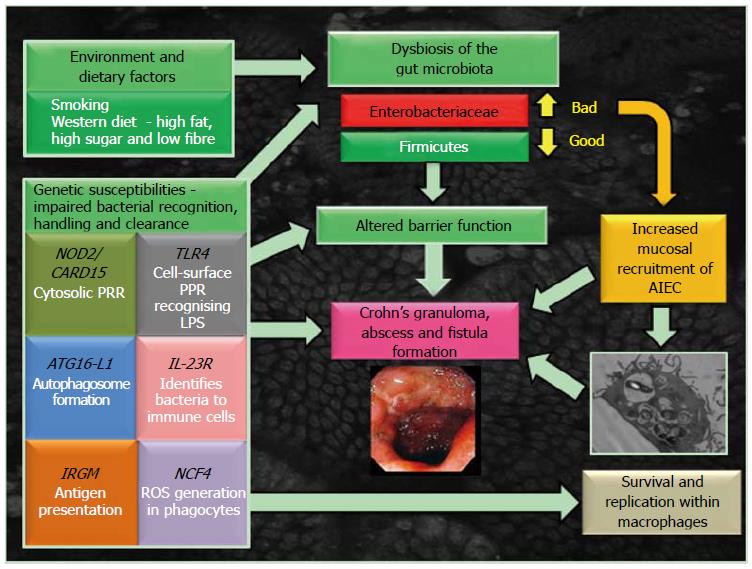
Figure 1 Model for the development of Crohn’s disease.
AIEC: Adherent, invasive Escherichia coli; ATG16L1: Autophagy-related 16-like 1; CARD15/NOD2: Caspase-recruitment domain 15/nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing-2 receptor; IL-23R: Interleukin-23 receptor; IRGM: Immunity-related GTPase M; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; NCF4: Neutrophil cytosolic factor-4 gene; PRR: Pathogen recognition receptor; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TLR4: Toll-like receptor 4.
-
Citation: Tawfik A, Flanagan PK, Campbell BJ.
Escherichia coli -host macrophage interactions in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(27): 8751-8763 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i27/8751.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i27.8751