Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2014; 20(26): 8525-8534
Published online Jul 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8525
Published online Jul 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8525
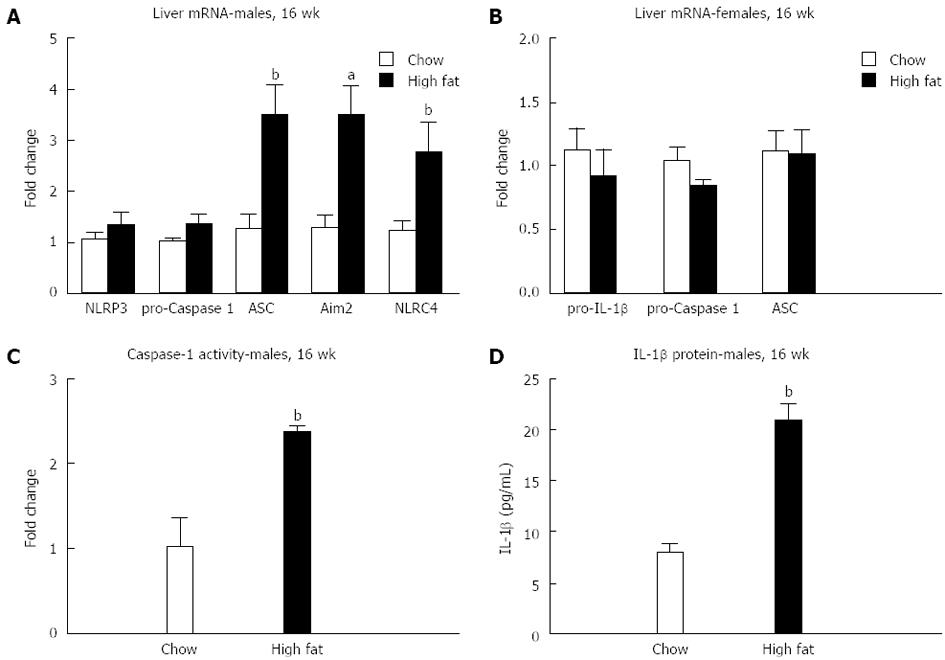
Figure 6 Long-term high fat diet induced inflammasome upregulation and activation in male mice.
Hepatic mRNA expression of the inflammasome components NOD-like receptors3 (NLRP3), caspase-1, adaptor molecule, Aim2, and NLRC4 were measured using real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction in male (A) and female (B) mice after a long-term high fat diet. The functional activity of the inflammasome was evaluated by measurements of caspase-1 activity (C) and total nterleukin (IL)-1β protein (D) levels, in the liver. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs chow fed controls, n = 10/group.
- Citation: Ganz M, Csak T, Szabo G. High fat diet feeding results in gender specific steatohepatitis and inflammasome activation. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(26): 8525-8534
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i26/8525.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8525