Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2014; 20(26): 8525-8534
Published online Jul 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8525
Published online Jul 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8525
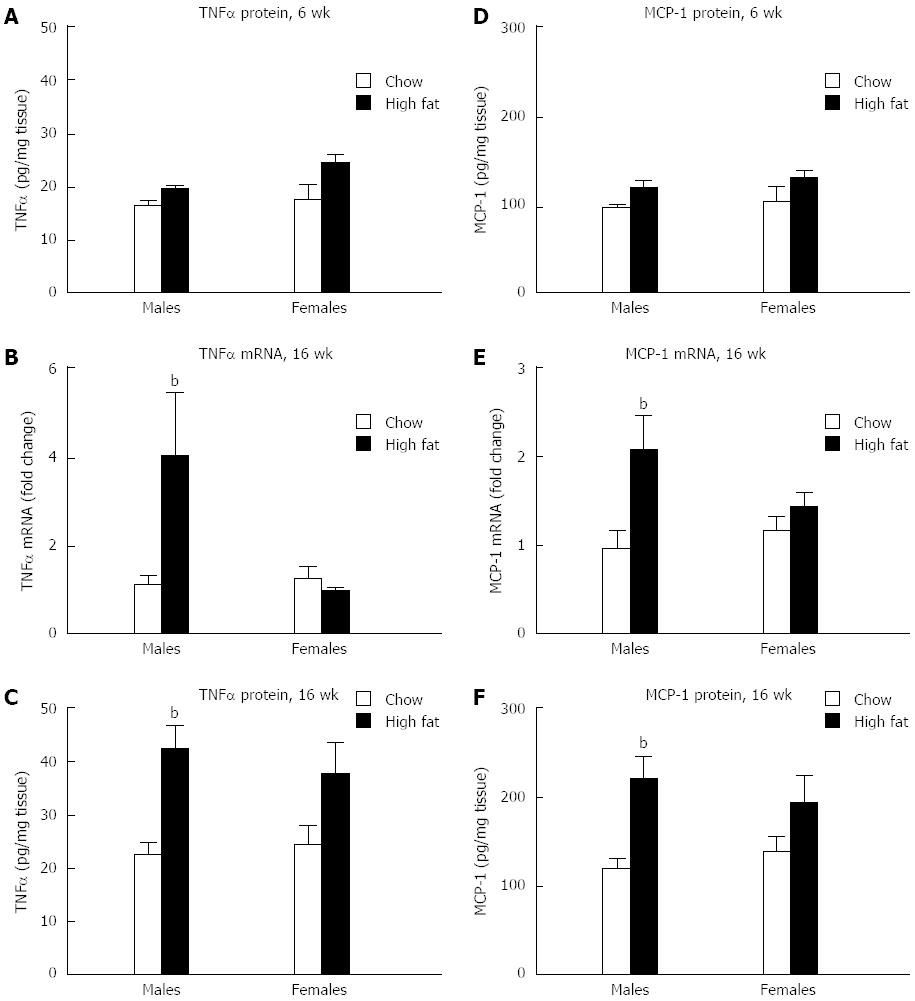
Figure 5 Long-term high fat diet results in hepatic inflammation in male mice.
A-C: Liver tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) protein levels (A) were evaluated in the short-term feeding levels of TNFα in the liver were analyzed at the mRNA (B) and protein (C) level after a long-term feeding; D-F: Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1) protein levels (D) were evaluated in the short-term feeding. Levels of MCP-1 in the liver were analyzed at the mRNA (E) and protein (F) level after a long-term feeding. bP < 0.01 vs chow fed controls, n = 10/group.
- Citation: Ganz M, Csak T, Szabo G. High fat diet feeding results in gender specific steatohepatitis and inflammasome activation. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(26): 8525-8534
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i26/8525.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8525