Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2014; 20(26): 8525-8534
Published online Jul 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8525
Published online Jul 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8525
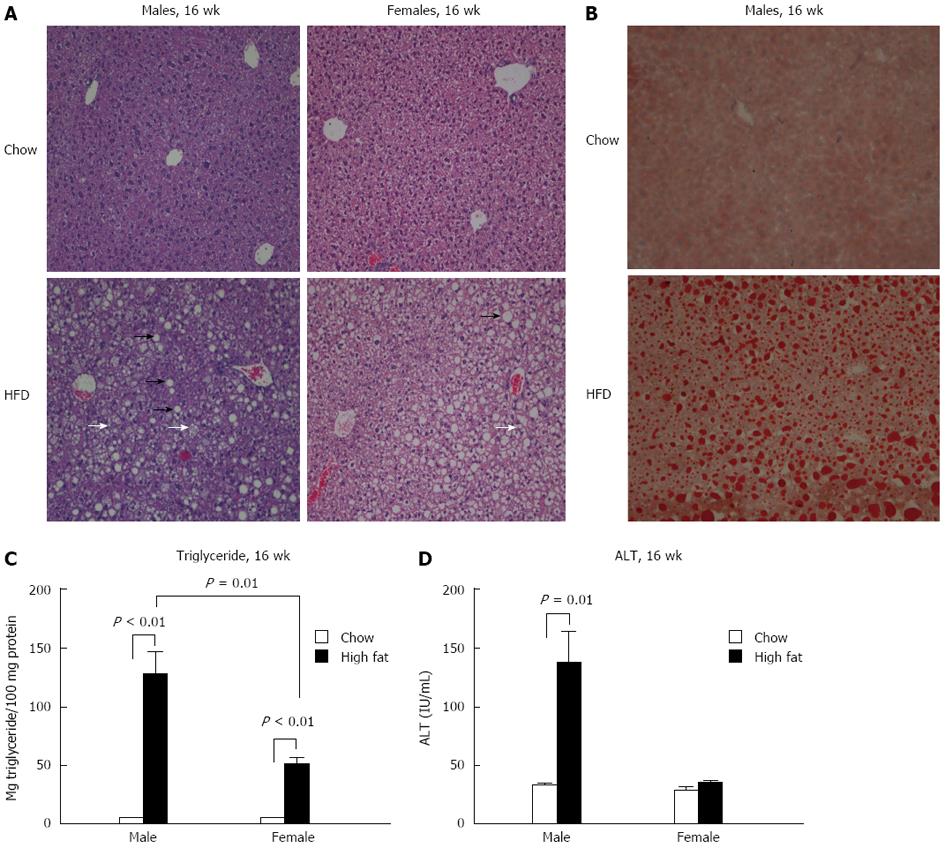
Figure 4 Long-term high fat diet feeding results in steatohepatitis in male mice, and steatosis in female mice.
Male and female mice were fed with either high fat diet (HFD) or control chow diet for 6 or 16 wk. A, B: Liver tissue was subjected to HE of male (A) and Oil-Red-O staining (B) (× 100). Dark arrow: Macrovesicular steatosis, white arrow: Microvesicular steatosis. One representative slide from n = 5/group is shown; C, D: Liver triglyceride levels (C) were evaluated in mice fed with HFD for 16 wk. Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels were measured after long-term HFD feeding (D).
- Citation: Ganz M, Csak T, Szabo G. High fat diet feeding results in gender specific steatohepatitis and inflammasome activation. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(26): 8525-8534
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i26/8525.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8525