Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2014; 20(26): 8471-8481
Published online Jul 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8471
Published online Jul 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8471
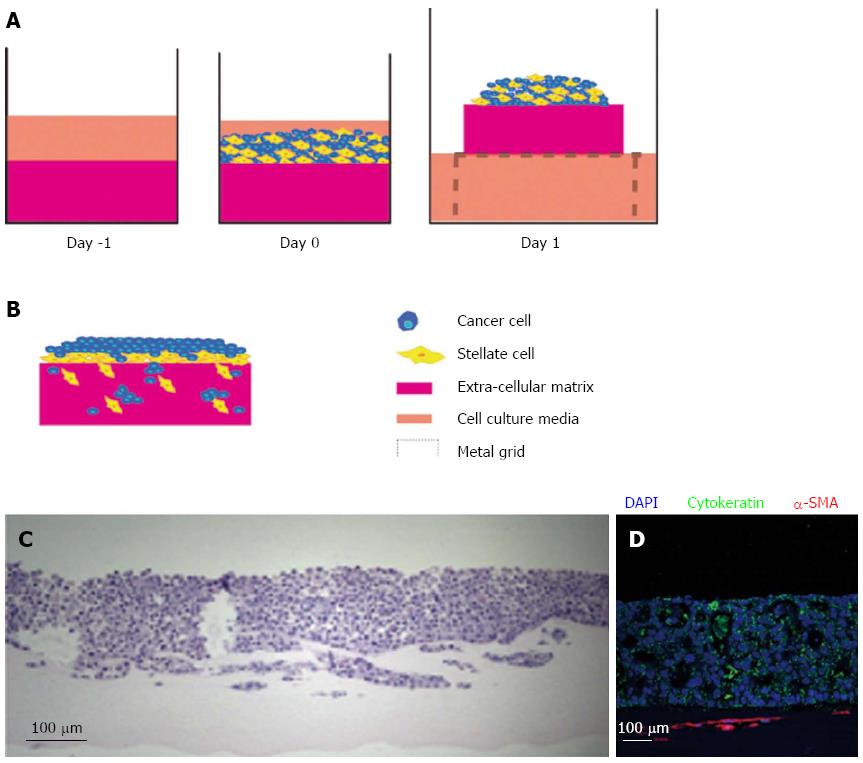
Figure 4 Raised organotypic model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with cancer cells and pancreatic stellate cell interaction.
A: Extracellular matrix gels containing were polymerised in 24-well plates before cancer stellate cells were seeded on top and allowed to interact and attach. These gels are then raised onto metal grids and fed from below creating a chemotactic gradient. Organotypic models were cultured for up to 14 d; B: Illustration of cancer cells and stellate cells in a raised model showing increased proliferation and invasion of both stellate and cancer cells into the gel; C: HE section of a raised gel with cancer cells and pancreatic stellate cells seeded on top; D: Immunofluorescence in the same gel showing strong cytokeratin expression in the cancer cells and α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression in the stellate cells which form a layer below the cancer cells.
- Citation: Coleman SJ, Watt J, Arumugam P, Solaini L, Carapuca E, Ghallab M, Grose RP, Kocher HM. Pancreatic cancer organotypics: High throughput, preclinical models for pharmacological agent evaluation. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(26): 8471-8481
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i26/8471.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8471