Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2014; 20(25): 8119-8129
Published online Jul 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8119
Published online Jul 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8119
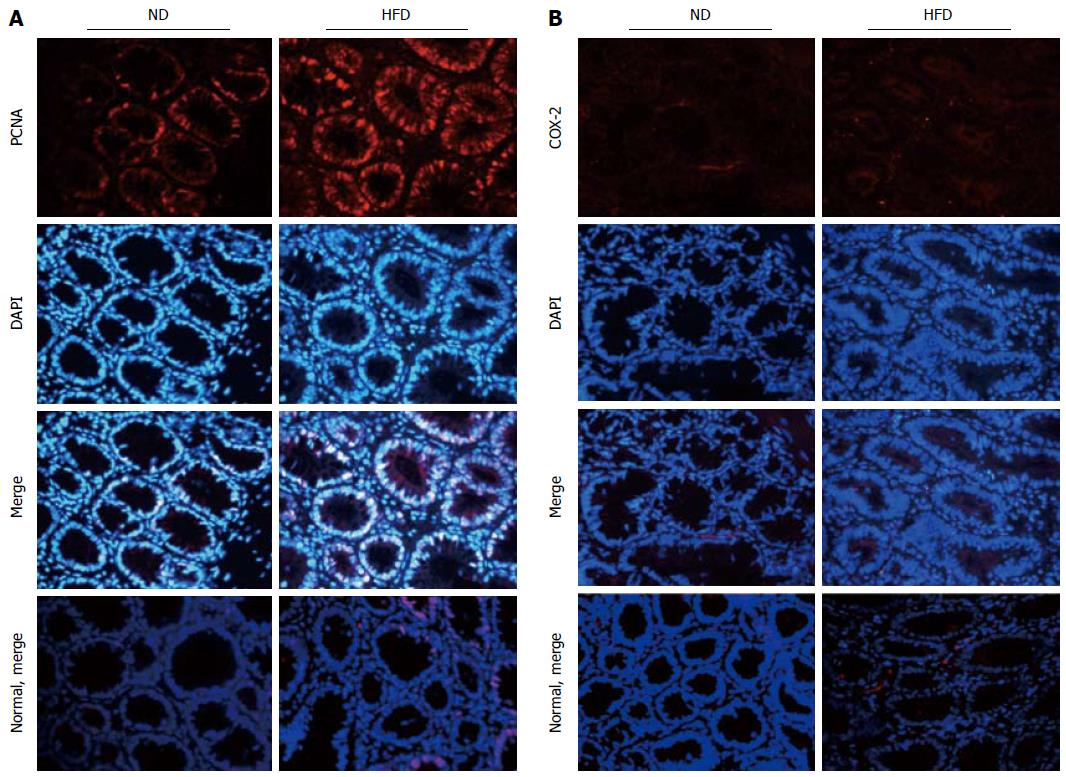
Figure 5 Expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and cyclooxygenase -2 in colonic adenoma and normal control tissue for both normal-fat diet and high-fat diet groups by immunofluorescence staining.
A: Representative images of immunofluorescence staining for proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA); B: Representative images of immunofluorescence staining for cyclooxygenase -2 (COX-2). The proteins are stained red with corresponding secondary antibody conjugated with Cy3, and cell nuclei are stained blue with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Imaging was documented at × 400 magnification. ND: Normal-fat diet; HFD: High-fat diet.
- Citation: Zhu QC, Gao RY, Wu W, Guo BM, Peng JY, Qin HL. Effect of a high-fat diet in development of colonic adenoma in an animal model. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(25): 8119-8129
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i25/8119.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8119