Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2014; 20(25): 8048-8054
Published online Jul 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8048
Published online Jul 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8048
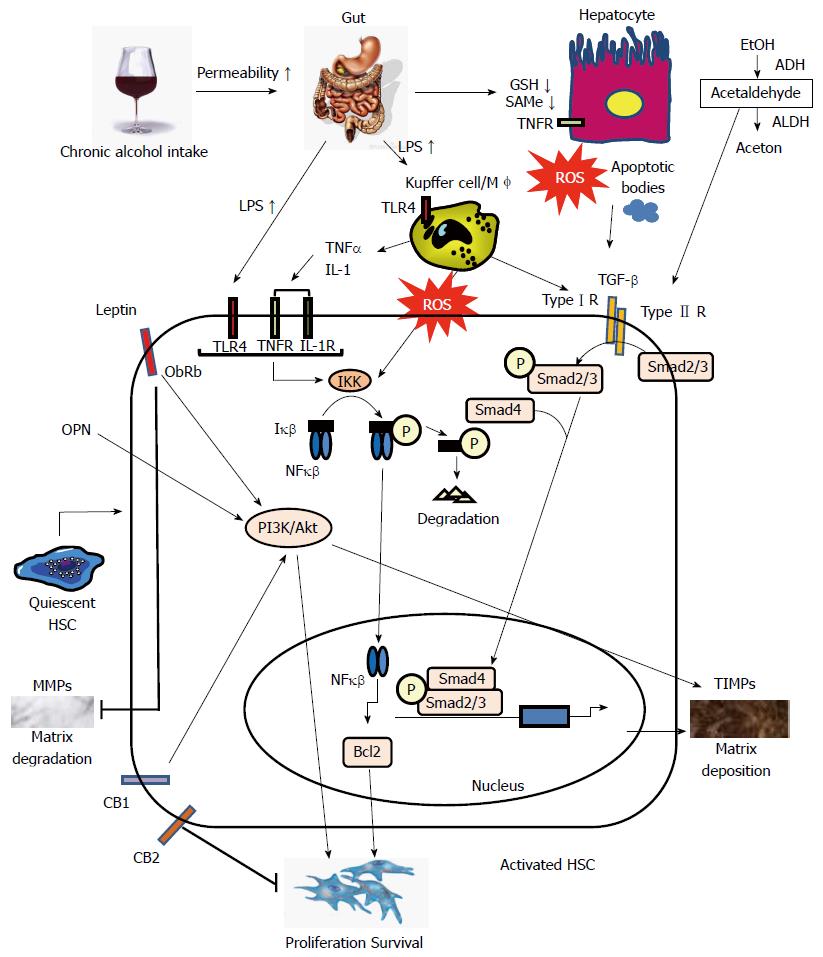
Figure 1 Signaling pathways regulating hepatic stellate cell activation in alcoholic liver disease.
Alcohol consumption causes hepatocyte damage, which subsequently induces apoptosis. Alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) oxidizes alcohol to acetaldehyde that is converted to acetate by acetaldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH). Acetaldehyde directly targets hepatic stellate cells (HSCs). Alcohol reduces glutathione (GSH) synthesis and acetaldehyde inhibits GSH activity in hepatocytes. Levels of the S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe) are also markedly reduced. Alcohol consumption increases permeability of the intestine to bacterial endotoxin that in turn, elevates serum lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels. LPS directly enhances HSCs activation by upregulating transforming growth factor (TGF)- signaling. TGF-β1 derived from activated Kupffer cells and damaged hepatocytes binds to TGF receptors. Phospho-Smad2/3 and Smad4 complexes translocate into the nucleus, display DNA-binding activity, and activate expression of genes related to fibrosis. Extracellular molecules, such as LPS, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1, and reactive oxygen species (ROS), activate IκB kinase (IKK) that, in turn, phosphorylates IκB, resulting in ubiquitination, dissociation of IκBα from nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), and eventually, degradation of IκB by the proteasome. The activated NF-κB is then translocated into the nucleus and binds to specific DNA response elements. NF-B-dependent pathways are involved in the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein B-cell lymphoma 2 (Bcl2). Leptin binds ObRb, activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway and inducing matrix deposition by increasing expression of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMPs). Leptin also inhibits matrix degradation by decreasing expression of Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). Osteopontin (OPN) positively stimulates the PI3K/Akt pathway. The cannabinoid receptor CB2 mediates antifibrotic actions; in contrast, activation of CB1 receptors positively stimulates the PI3K/Akt pathway to promote the proliferation and apoptosis of HSCs. TLR: Toll-like receptor.
- Citation: Fujii H, Kawada N. Fibrogenesis in alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(25): 8048-8054
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i25/8048.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8048