Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2014; 20(24): 7914-7925
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7914
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7914
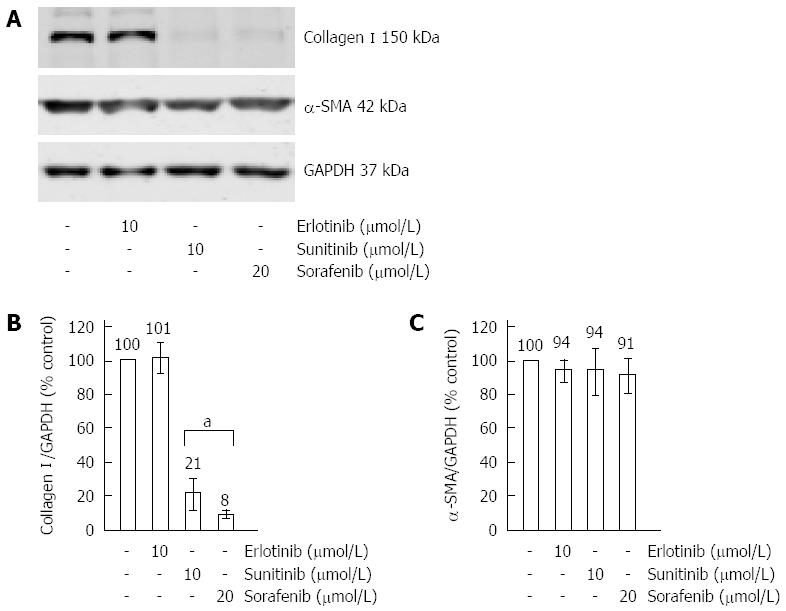
Figure 4 Effects of erlotinib, sorafenib and sunitinib on the expression of type I collagen and α-smooth muscle actin.
Cultured pancreatic stellate cells (PSC) were grown to subconfluency before they were treated for 48 h with SMI at the indicated concentrations. Afterwards, protein extracts from equal amounts of cells were subjected to Western blot analysis. Type I collagen, α-SMA and GAPDH (for loading control) were detected using fluorescein (IRDye®)-labelled secondary antibodies. (A) One representative Western blot for all three SMI is shown. Afterwards, fluorescence signal intensities of collagen I (B), α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) (C) and GAPDH (B and C) were quantified using Odyssey® software. Subsequently, the ratios collagen I/GAPDH (B) and α-SMA/GAPDH (C) were determined to normalize for loading variations. A ratio of one hundred percent corresponds to control cells cultured without SMI. Data of n = 6 independent experiments were used to calculate mean ± SE. aP < 0.05 vs control cultures.
- Citation: Elsner A, Lange F, Fitzner B, Heuschkel M, Krause BJ, Jaster R. Distinct antifibrogenic effects of erlotinib, sunitinib and sorafenib on rat pancreatic stellate cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(24): 7914-7925
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i24/7914.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7914