Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2014; 20(24): 7864-7877
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7864
Published online Jun 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7864
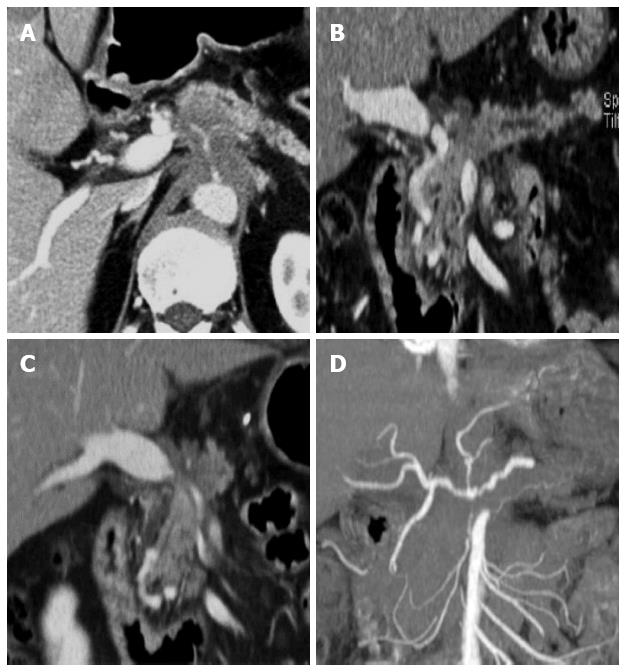
Figure 4 Post-process of multi-detector computed tomography for pancreatic cancer.
A: In the axial CT scan, an ill-defined pancreatic body cancer invading the celiac axis is identified; B: On the curved MPR along the pancreatic duct, the relationship between the pancreatic duct and the cancer can be more easily understood; C, D: The extent and degree of major vascular involvement caused by the pancreatic cancer can be comprehensively assessed using MPR and the maximum intensity projections. MDCT: Multi-detector computed tomography; MPR: Multiplanar reformations.
- Citation: Lee ES, Lee JM. Imaging diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: A state-of-the-art review. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(24): 7864-7877
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i24/7864.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i24.7864