Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2014; 20(23): 7260-7276
Published online Jun 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7260
Published online Jun 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7260
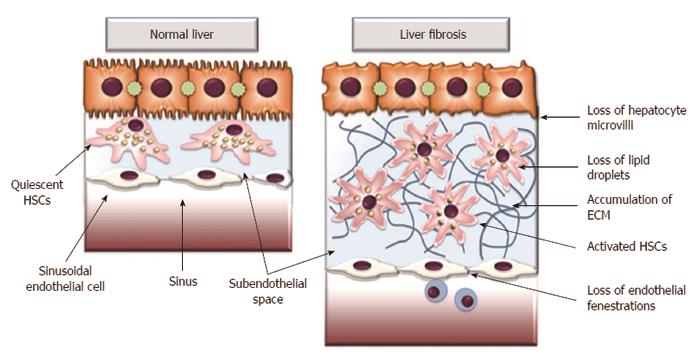
Figure 1 Extracellular matrix accumulation in subendothelial space activates quiescent hepatic stellate cells leading to the loss of hepatocyte microvilli and disappearance of endothelial fenestrations.
These architectural changes impair transport of solutes from the sinusoid to the hepatocytes, further contributing to the hepatocyte damage. ECM: Extracellular matrix; HSCs: Hepatic stellate cells.
- Citation: Elpek G&. Cellular and molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis: An update. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(23): 7260-7276
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i23/7260.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7260