Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2014; 20(23): 7104-7122
Published online Jun 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7104
Published online Jun 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7104
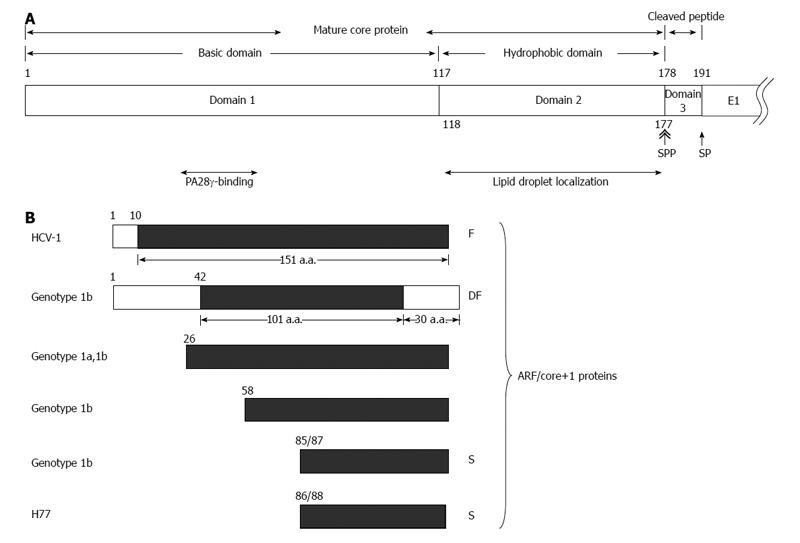
Figure 1 Various hepatitis C virus core gene products.
A: The hepatitis C virus (HCV) polyprotein is cleaved at residues 191/192 by the host signal peptidase (SP) and further cleaved at residue 177/178 by signal peptide peptidase (SPP) to release the mature core protein (a.a. 1-177) and the cleaved peptide (a.a. 178-191) from the precursor polyprotein. The mature core protein consists of the positively charged domain 1 (a.a. 1-117) and the hydrophobic domain 2 (a.a. 118-177). The highly basic domain 1 is involved in RNA-binding and its oligomerization. The region containing residues 44-71 of domain 1 binds to PA28γ. Domain 2 is involved in the association of HCV core protein with lipid droplets; B: Different alternative reading frame (ARF)/core+1 proteins from different HCV isolates/genotypes. The polypeptides from the conventional open reading frame are marked by empty rectangles while those from the alternative reading frame (ARF/core+1) by filled rectangles. The termination codon of ARF/core+1 proteins from other isolates/genotypes may be different from those shown in this figure.
- Citation: Li HC, Ma HC, Yang CH, Lo SY. Production and pathogenicity of hepatitis C virus core gene products. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(23): 7104-7122
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i23/7104.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7104