Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2014; 20(22): 6897-6905
Published online Jun 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.6897
Published online Jun 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.6897
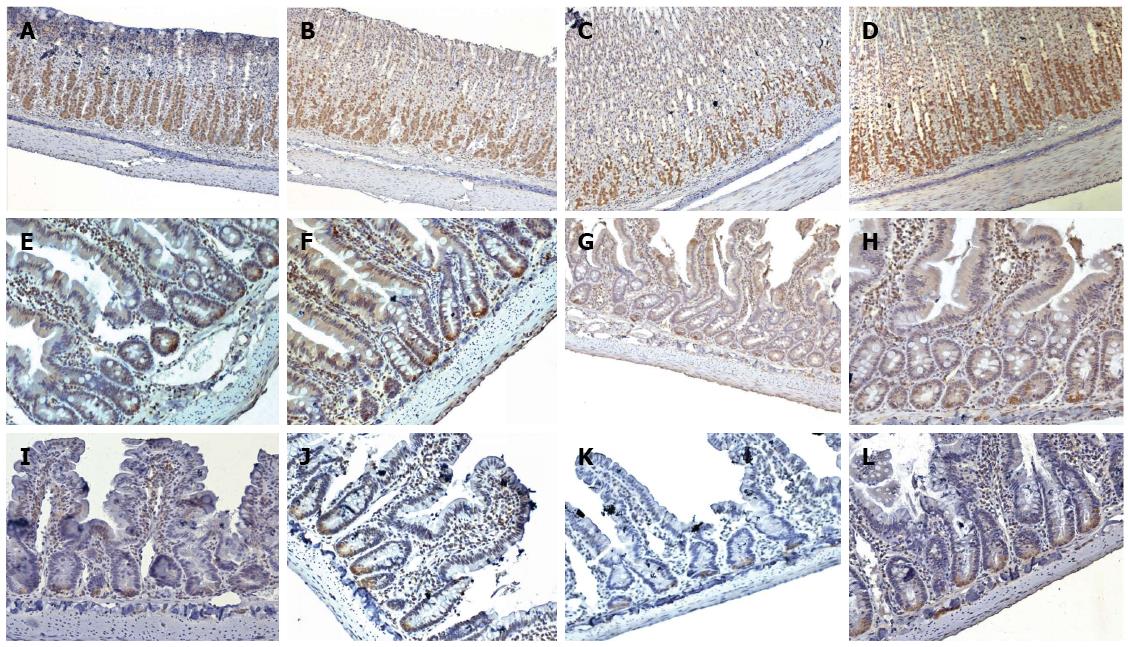
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical localisation of nesfatin-1 in the gastrointestinal tissues.
A-D: Nesfatin-1 IR cells (brown) in the stomach of VMH-lesioned, VMH-sham, VLH-lesioned, and VLH-sham rats, respectively; E-H: Nesfatin-1 IR cells (brown) in the duodenum of VMH-lesioned, VMH-sham, VLH-lesioned, and VLH-sham rats, respectively; I-L: Nesfatin-1 IR cells (brown) in the small intestine of VMH-lesioned, VMH-sham, VLH-lesioned, and VLH-sham rats, respectively. All of the magnifications are × 200 with the exception of the stomach, which is × 100. VMH: Ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus; VLH: Ventrolateral hypothalamic nucleus; IR: Immunoreactive.
- Citation: Tian ZB, Deng RJ, Sun GR, Wei LZ, Kong XJ, Ding XL, Jing X, Zhang CP, Ge YL. Expression of gastrointestinal nesfatin-1 and gastric emptying in ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus- and ventrolateral hypothalamic nucleus-lesioned rats. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(22): 6897-6905
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i22/6897.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.6897