Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2014; 20(20): 6262-6278
Published online May 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6262
Published online May 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6262
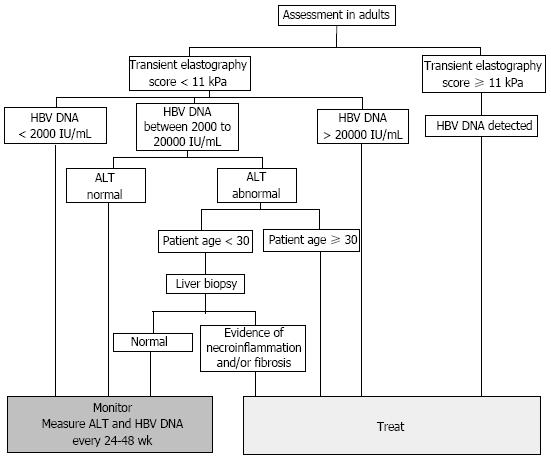
Figure 2 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence algorithm for initiation of treatment in chronic hepatitis B infection.
Current indications for treatment are based on a combination of levels of serum hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA, serum alanine transaminase (ALT), and the severity of liver disease. Specifically, patients with a transient elastography score ≥ 11 kPa are likely to have cirrhosis and confirmation by liver biopsy is not needed. Abnormal ALT, measured by two consecutive tests conducted 3 mo apart, is defined as ≥ 30 IU/mL in males, and ≥ 19 IU/mL in females.
- Citation: Tang CM, Yau TO, Yu J. Management of chronic hepatitis B infection: Current treatment guidelines, challenges, and new developments. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(20): 6262-6278
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i20/6262.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6262