Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2014; 20(20): 6252-6261
Published online May 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6252
Published online May 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6252
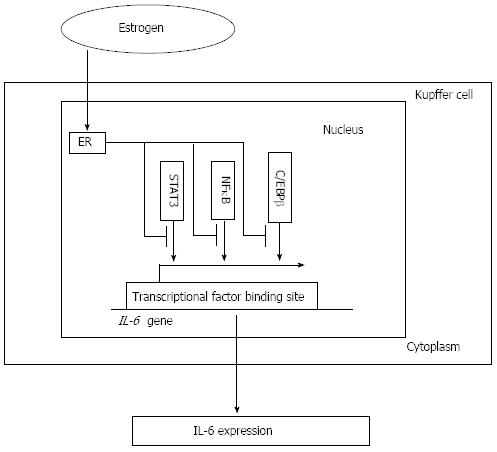
Figure 3 Interleukin-6 expression and estrogen receptor signaling pathway.
By decreasing the activity of core factors such as NFκB, STAT3 and C/EBPβ, which is associated with the interleukin-6 (IL-6) promoter activity and required for the production of IL-6 in vivo and in vitro, estrogen combines with the estrogen receptor (ER) signaling pathway to decrease the IL-6 level and attenuate its induction of liver injury. NFκB: Nuclear factor κB; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; C/EBPβ: CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein β.
- Citation: Liu WC, Liu QY. Molecular mechanisms of gender disparity in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(20): 6252-6261
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i20/6252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6252