Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2014; 20(20): 6252-6261
Published online May 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6252
Published online May 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6252
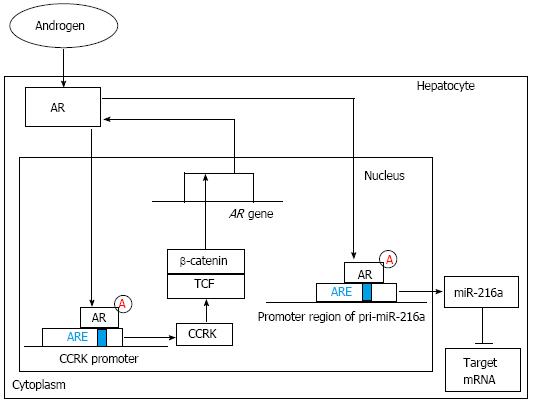
Figure 2 The regulation and function of androgen receptor signaling pathway.
On one hand, ligand-activated androgen receptor (AR) can increase cell cycle-related kinase (CCRK) expression through directly binding to androgen-responsive element (ARE) of the CCRK promoter region and stimulate its transcription and expression. Ectopic expression of CCRK in immortalized human liver cells activated β-catenin/T cell factor (TCF) signaling to stimulate cell cycle progression and to induce AR expression. On the other hand, ligand-stimulated AR can increase miR-216a transcription by directly binding to the ARE site within the promoter region of pri-miR-216a, which can lead to the elevation of the miR-216a level and the subsequent suppression of its target genes including some tumor suppressors. Finally, the early stage of hepatocarcinogenesis, including increased cell proliferation and enhanced migration and invasive activities of hepatocytes, is partly initiated.
- Citation: Liu WC, Liu QY. Molecular mechanisms of gender disparity in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(20): 6252-6261
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i20/6252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i20.6252