Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2014; 20(2): 498-508
Published online Jan 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.498
Published online Jan 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.498
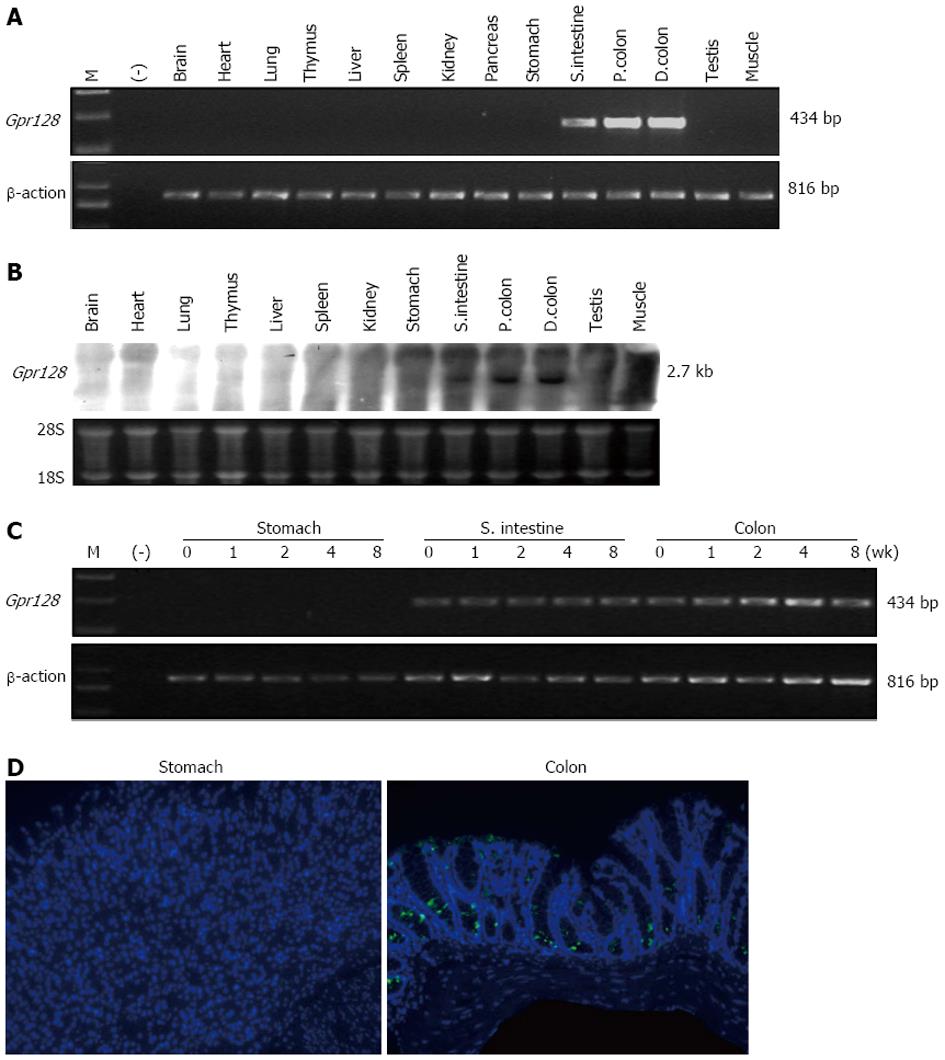
Figure 2 Selective expression of Gpr128 within the intestine in mice.
A: Expression levels of Gpr128 mRNA. The mRNA levels were examined in major tissues of normal mice using semi-quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), and the expression level of β-actin was used as an endogenous control. M: Marker lane; (-): Negative control without template; B: Northern blotting analysis of Gpr128. Total RNA from wild type mice was extracted and subjected to Northern blotting analysis using a 715-bp fragment of Gpr128 cDNA corresponding to exons 1 through 6. The bottom lane shows the 28S and 18S ribosomal RNA as a control; C: Examination of the stage-specific expression of Gpr128 mRNA. RT-PCR was performed throughout the digestive tract and at various postnatal developmental stages to determine the presence of Gpr128 mRNA from postnatal day 0 through 8 wk; D: Expression pattern of Gpr128 protein in the stomach and colon of adult WT mouse revealed by immunofluorescence (original magnification, × 200).
-
Citation: Ni YY, Chen Y, Lu SY, Sun BY, Wang F, Wu XL, Dang SY, Zhang GH, Zhang HX, Kuang Y, Fei J, Gu MM, Rong WF, Wang ZG. Deletion of
Gpr128 results in weight loss and increased intestinal contraction frequency. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(2): 498-508 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i2/498.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.498