Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2014; 20(19): 5839-5848
Published online May 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i19.5839
Published online May 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i19.5839
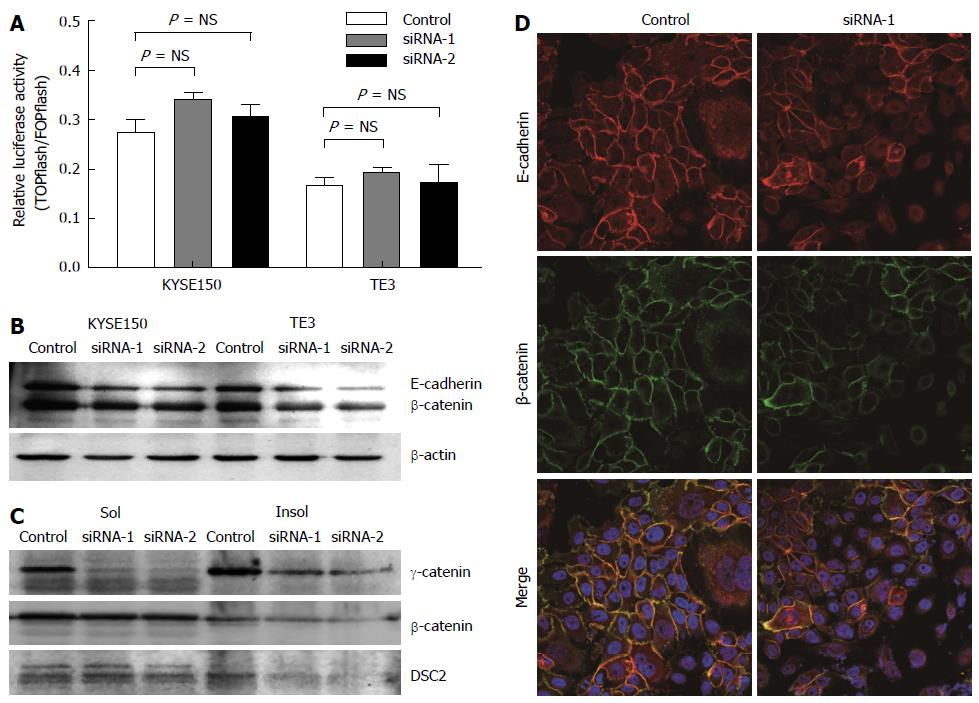
Figure 3 γ-catenin affects cell motility through cell-cell adhesion-dependent mechanisms.
A: TOPflash reporter activity in KYSE150 and TE3 cells. Cells were co-transfected with either TOPflash or FOPflash reporter plasmids along with siRNA-1/-2 or control siRNA. The level of β-catenin-dependent transcription was determined by TOPflash luciferase activity. FOPflash reporter plasmids containing mutant β-catenin/ TCF-binding sites were used as controls. Data represent the results of triplicate dishes from two independent experiments; B: Western blot analyses of E-cadherin and total β-catenin in γ-catenin-specific siRNA or control-transfected esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells. β-actin served as a loading control; C: Western blot analyses of triton X-100-soluble and -insoluble γ-catenin, β-catenin and DSC2 proteins in γ-catenin-specific siRNA or control-transfected ESCC cells; D: The subcellular localizations of β-catenin and E-cadherin was examined using immunofluorescence analysis. Of note, knocking down γ-catenin expression caused reduced β-catenin and E-cadherin membrane localization.
- Citation: Fang WK, Liao LD, Gu W, Chen B, Wu ZY, Wu JY, Shen J, Xu LY, Li EM. Down-regulated γ-catenin expression is associated with tumor aggressiveness in esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(19): 5839-5848
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i19/5839.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i19.5839