Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 21, 2014; 20(19): 5839-5848
Published online May 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i19.5839
Published online May 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i19.5839
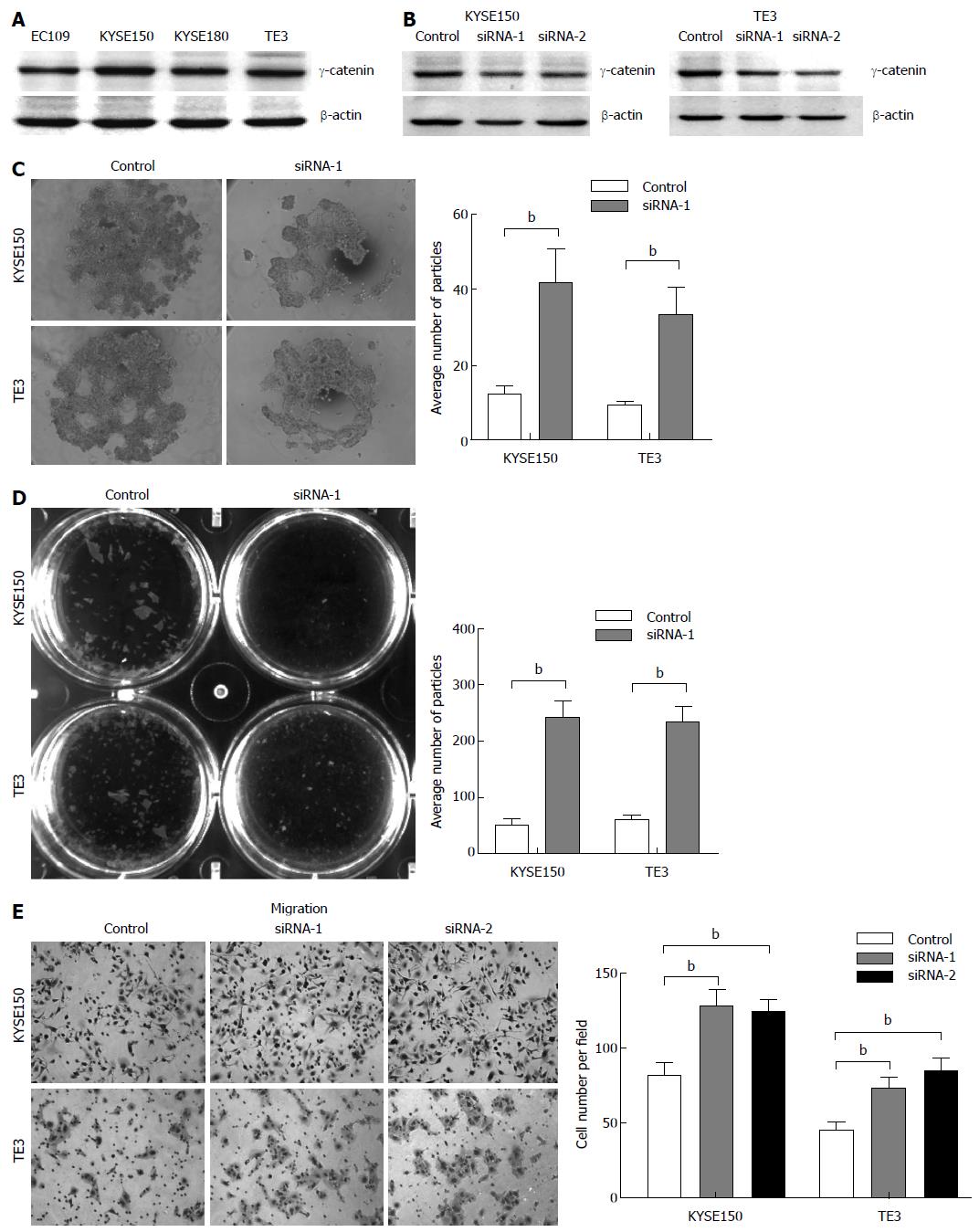
Figure 2 Alterations of cell-cell adhesion and cell migration exerted by RNAi-mediated knockdown of γ-catenin.
A: Representative Western blot of γ-catenin in 4 esophageal cancer cell lines; B: KYSE150 and TE3 cells were transfected with γ-catenin siRNAs (siRNA-1 and -2), or a negative control siRNA (control). Western blot analysis was used to show RNAi-mediated knockdown. Equal loading was ascertained using β-actin as an internal control; C: Hanging drop assay. Cells were seeded into hanging drop cultures and allowed to aggregate for 24 h. After trituration by passing the cell cluster 30 times through a 200 μL pipette tip, the degree of dissociation of the cell cluster was visualized by microscopy and quantified by manual counting under a dissecting microscope; D: Dispase-based dissociation assay. Cell monolayers were separated from culture dishes via incubation with dispase. Monolayers were transferred to 15 mL conical tubes containing 2 mL of phosphate buffered saline. After 50 inversions, the degree of fragmentation of the monolayers was observed. The dissociation assay was quantified by counting the number of total particles; E: Transwell assay was performed to determine cell migration. Migrated cells were fixed and stained, and representative fields were photographed. The cells were quantified in 10 random fields with a light microscope (× 200). The mean value was calculated from data obtained from three separate chambers. bP < 0.01 vs the control group.
- Citation: Fang WK, Liao LD, Gu W, Chen B, Wu ZY, Wu JY, Shen J, Xu LY, Li EM. Down-regulated γ-catenin expression is associated with tumor aggressiveness in esophageal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(19): 5839-5848
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i19/5839.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i19.5839