Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2014; 20(18): 5177-5190
Published online May 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5177
Published online May 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5177
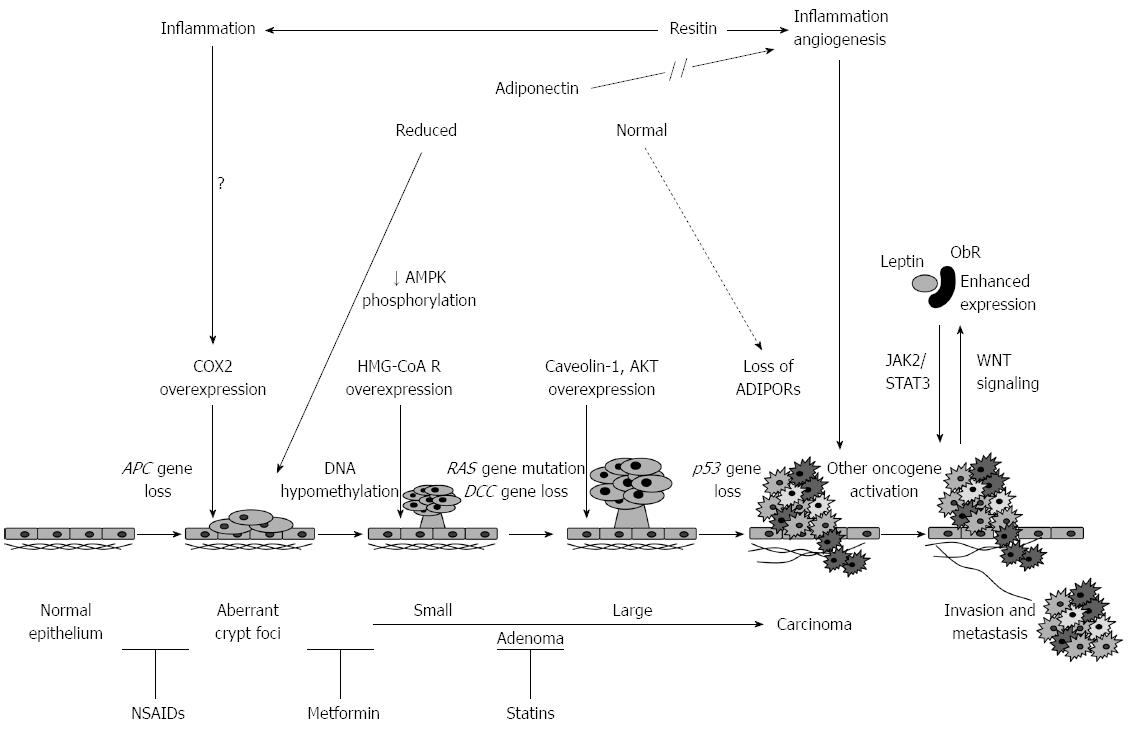
Figure 3 Scheme depicting the stages of normal epithelium-to-carcinoma sequence and the potential factors that relate obesity and colorectal cancer progression.
ADIPORs: Adiponectin receptors; AKT: Serine/threonine-protein kinase; AMPK: Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; APC: Adenomatous polyposis coli; COX2: Cyclooxygenase-2; DCC: Deleted in colorectal carcinoma; HMG-CoA R: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase; JAK: Janus kinase; ObR: Leptin receptor; STAT: Signal transducers and activators of transcription.
- Citation: Riondino S, Roselli M, Palmirotta R, Della-Morte D, Ferroni P, Guadagni F. Obesity and colorectal cancer: Role of adipokines in tumor initiation and progression. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(18): 5177-5190
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i18/5177.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i18.5177