Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2014; 20(17): 5141-5146
Published online May 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5141
Published online May 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5141
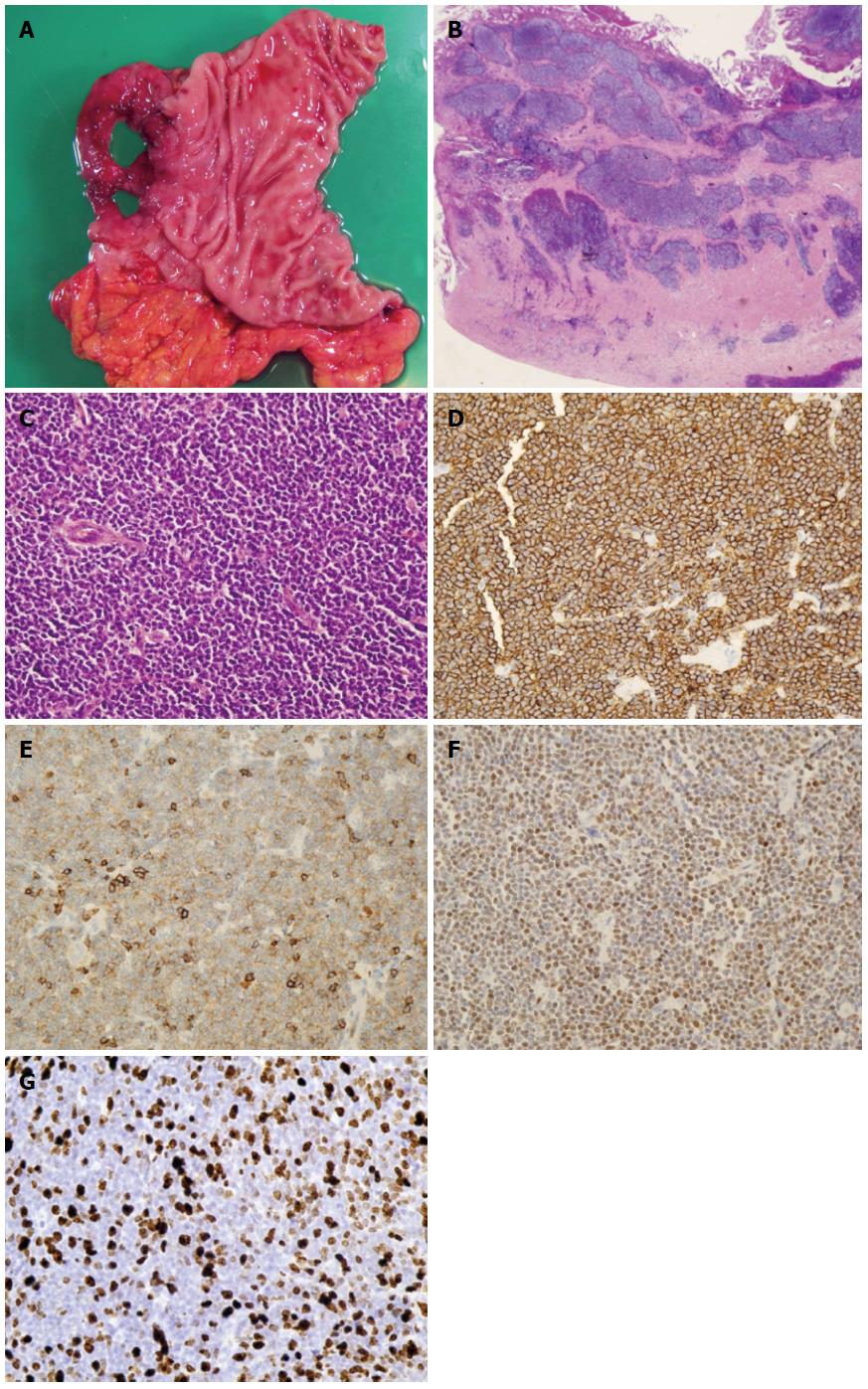
Figure 3 Pathological findings.
A: Macroscopic specimen showed perforation in the duodenal bulb; B: Histopathologically, lymphoma lesion in the duodenal bulb invaded deep into the muscularis propria (HE stain, x 20); C: Tumor cells varying in size from small to middle-sized densely proliferated (HE stain, x 200); D-F: These tumor cells were positive on immunohistochemical staining for CD20 (D), CD5 (E), and Cyclin D1 (F), findings compatible with mantle cell lymphoma (x 200); G: Ki-67 proliferative (MIB-1) index in the duodenal bulb was 50.2% (1397 cells/2781 cells) (x 200).
- Citation: Saito M, Miyazaki M, Tanino M, Tanaka S, Miyashita K, Izumiyama K, Mori A, Irie T, Tanaka M, Morioka M, Tsukamoto E. 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging for a gastrointestinal mantle cell lymphoma with multiple lymphomatous polyposis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(17): 5141-5146
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i17/5141.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5141