Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2014; 20(17): 5141-5146
Published online May 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5141
Published online May 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5141
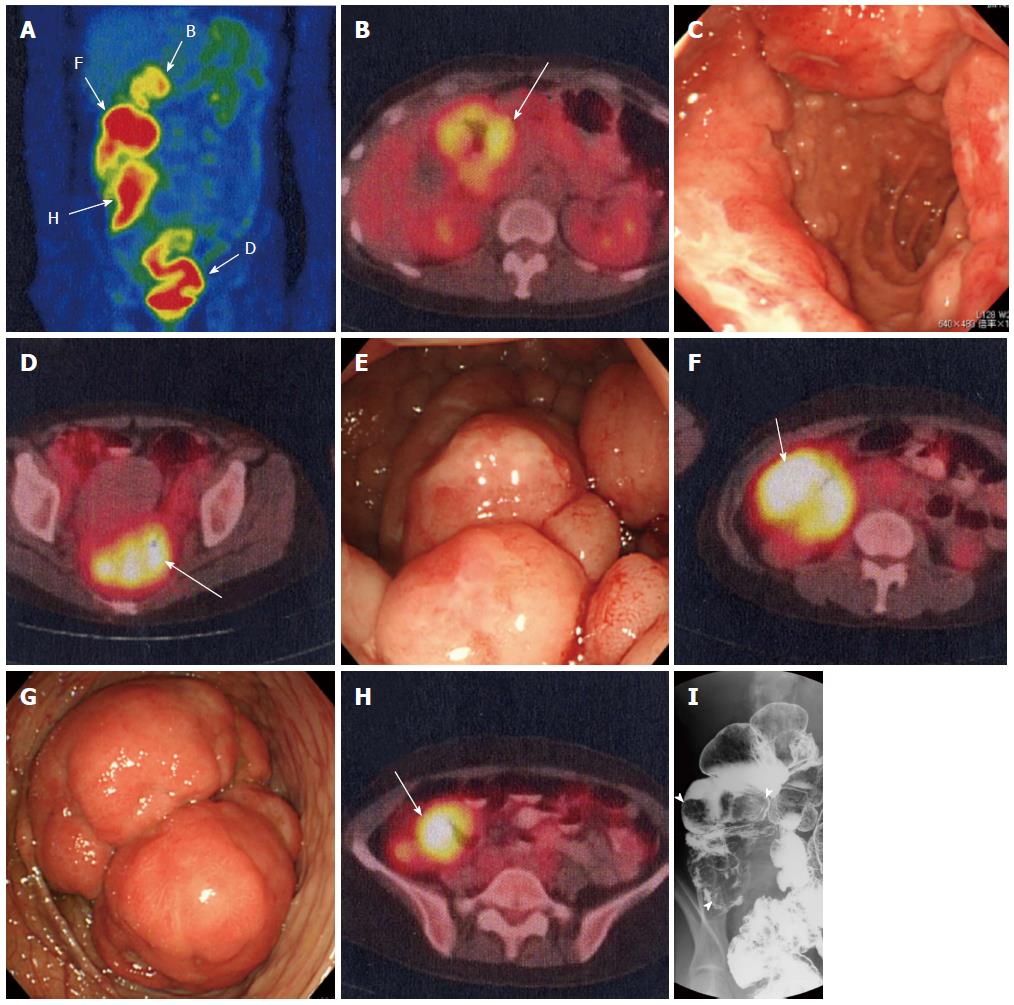
Figure 2 Images of atypical type multiple lymphomatous polyposis.
A, B, D, F, H: [fluorine-18]-fluorodeoxy-glucose -positron emission tomography/computed tomography: (A) Uptake in the gastrointestinal tract was noted at the 4 sites shown in longitudinal images. The SUVmax was 5.1, 6.9, 7.7, and 6.5 in the duodenal bulb (B), rectum (D), ascending colon (F), and cecum (H), respectively; C: Gastrointestinal endoscopy: Three large tumorous lesions circumferentially surrounding the duodenal bulb were observed; E, G: Colonoscopy: Multiple larger nodules than usual type MLP were observed in the rectum (E). The ascending colon was intussuscepted due to a large tumor (G); I: X-ray imaging of the ascending colon and cecum: Large tumorous lesions were observed in the ascending colon and cecum (arrowheads).
- Citation: Saito M, Miyazaki M, Tanino M, Tanaka S, Miyashita K, Izumiyama K, Mori A, Irie T, Tanaka M, Morioka M, Tsukamoto E. 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging for a gastrointestinal mantle cell lymphoma with multiple lymphomatous polyposis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(17): 5141-5146
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i17/5141.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5141