Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2014; 20(17): 5066-5073
Published online May 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5066
Published online May 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5066
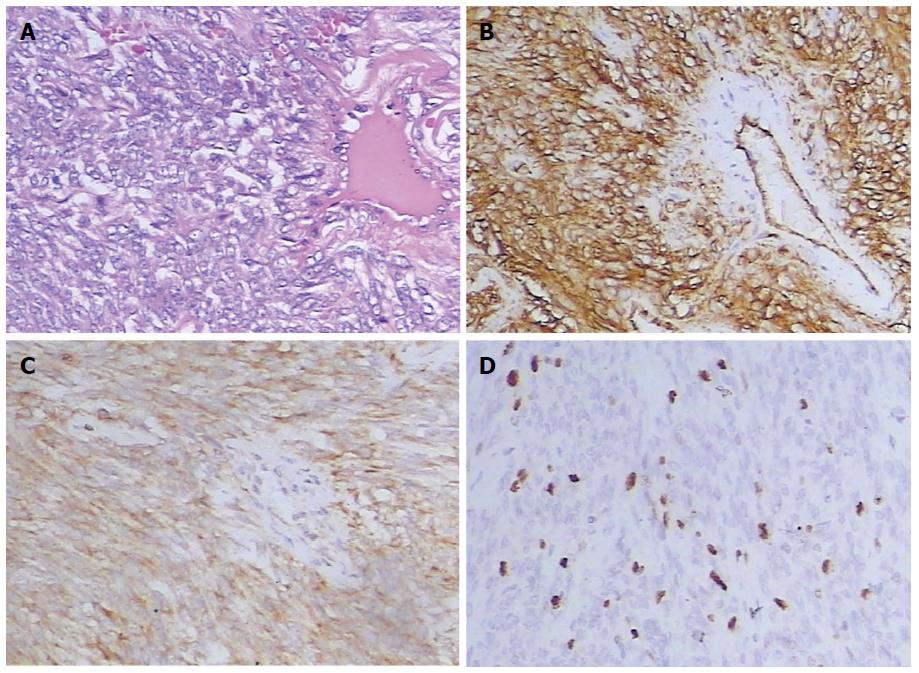
Figure 4 Pathologic features of the solitary fibrous tumor.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 40, indicates monotonous spindle cell proliferation with a hemangiopericytoma-like vascular growth pattern; B-D: Immunohistochemical staining, x 40, indicates that the tumor is diffusely positive for CD34 (B) and Bcl-2 (C), and the proportion of Ki67 positive cells is 15% (D).
- Citation: Li XM, Reng J, Zhou P, Cao Y, Cheng ZZ, Xiao Y, Xu GH. Solitary fibrous tumors in abdomen and pelvis: Imaging characteristics and radiologic-pathologic correlation. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(17): 5066-5073
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i17/5066.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5066