Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2014; 20(17): 5066-5073
Published online May 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5066
Published online May 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5066
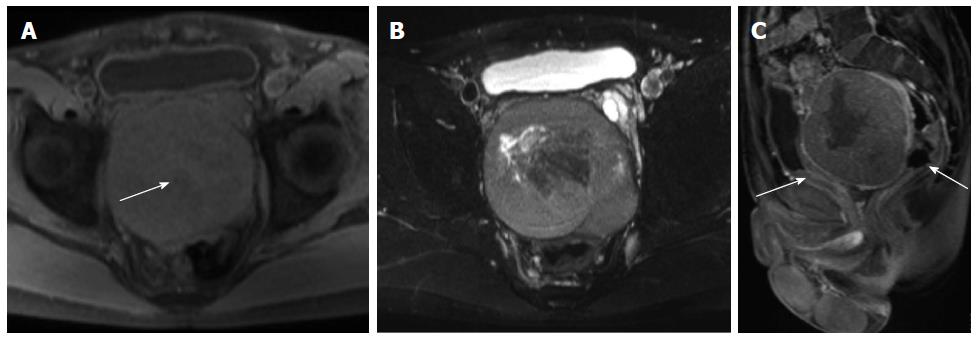
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance images of a solitary fibrous tumor in the rectovesical space.
A: T1-weighted Magnetic resonance (MR) image showing an oval isointense mass with patchy mild hyperintensity (arrow). The patchy mild hyperintensity was proven to be a hemorrhage; B: Fat-suppressed T2-weighted MR images reveal a mass with heterogeneous hyperintensity and patchy hypointensity; C: Contrast-enhanced MR images demonstrate moderate heterogeneous enhancement of the mass, which displaces the bladder anteriorly and rectum posteriorly (arrows).
- Citation: Li XM, Reng J, Zhou P, Cao Y, Cheng ZZ, Xiao Y, Xu GH. Solitary fibrous tumors in abdomen and pelvis: Imaging characteristics and radiologic-pathologic correlation. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(17): 5066-5073
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i17/5066.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.5066