Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 7, 2014; 20(17): 4953-4962
Published online May 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.4953
Published online May 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.4953
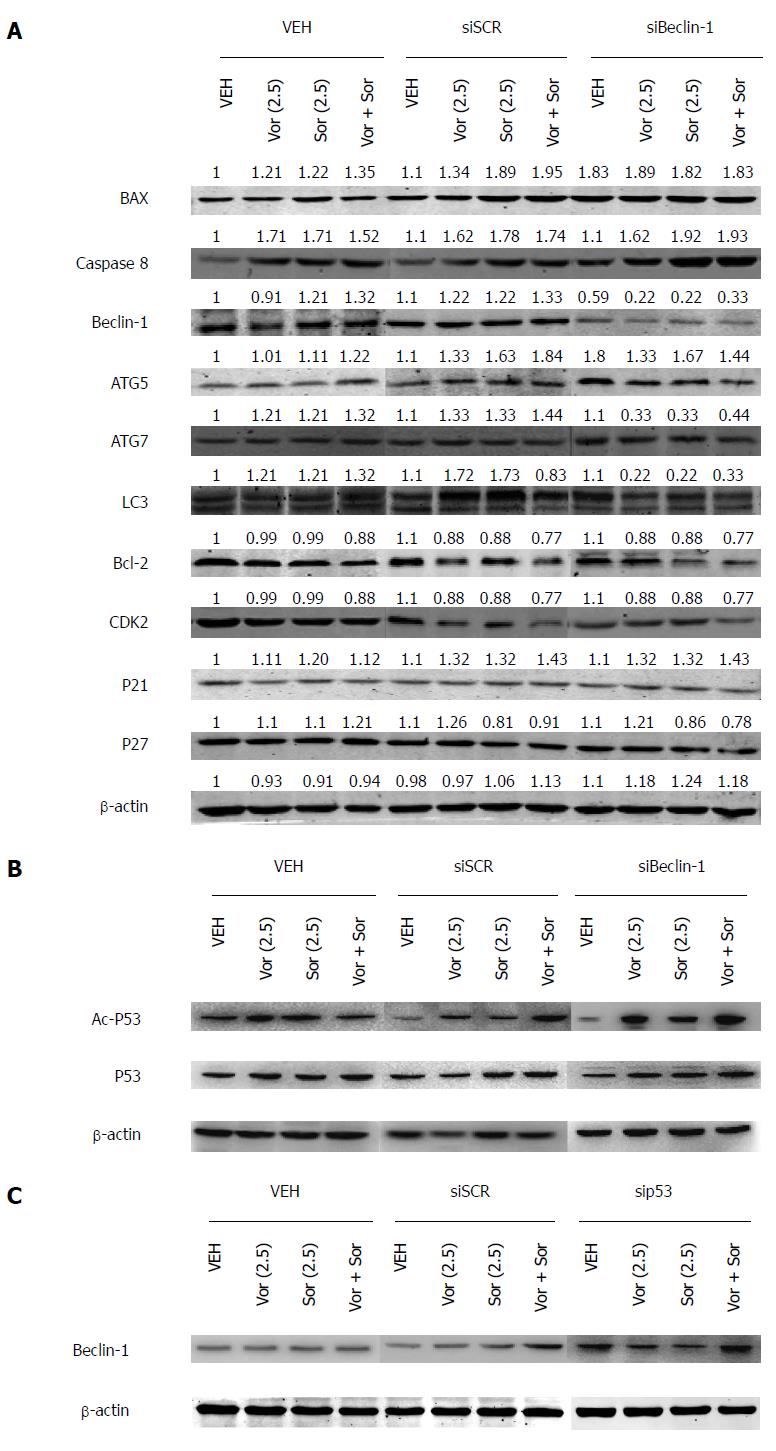
Figure 3 Sorafenib, vorinostat, or the drug combination induces the modulation of apoptosis-, cell cycle- and autophagy-related proteins.
A: Representative images of Western blot showing the effect of treatment with siBeclin-1 and vorinostat/sorafenib on apoptosis-, cell cycle-, and autophagy-related proteins in HepG2 cells. siSCR, siRNA scramble; B: Representative images of Western blot showing the acetylated p53 level in HepG2 cells treated with or without siBeclin-1 or vorinostat/sorafenib. siSCR, siRNA scramble; C: Protein level of Beclin-1 in HepG2 cells infected with sip53 combined with or without vorinostat/sorafenib. All experiments were performed independently in triplicate. siSCR, siRNA scramble.
- Citation: Yuan H, Li AJ, Ma SL, Cui LJ, Wu B, Yin L, Wu MC. Inhibition of autophagy significantly enhances combination therapy with sorafenib and HDAC inhibitors for human hepatoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(17): 4953-4962
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i17/4953.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i17.4953