Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2014; 20(16): 4771-4777
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4771
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4771
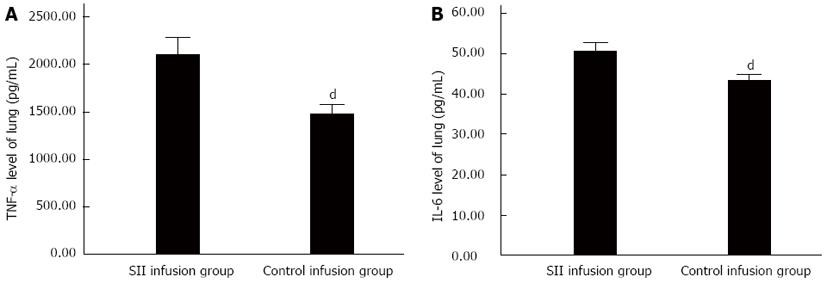
Figure 2 Tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6 levels in lung tissues.
Severe intraperitoneal infection (SII) lymph infusion enhances sepsis-induced inflammatory cytokine responses in the lung. Concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-α (A) and interleukin (IL)-6 (B) were measured from lung extracts of SII and control lymph-infused rats. Data are mean ± SD of 10 rats in each group. Results are representative of two separate experiments. dP < 0.01 vs SII infusion group.
- Citation: Zhang YM, Zhang SK, Cui NQ. Intravenous infusion of mesenteric lymph from severe intraperitoneal infection rats causes lung injury in healthy rats. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(16): 4771-4777
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i16/4771.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4771