Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2014; 20(16): 4761-4770
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4761
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4761
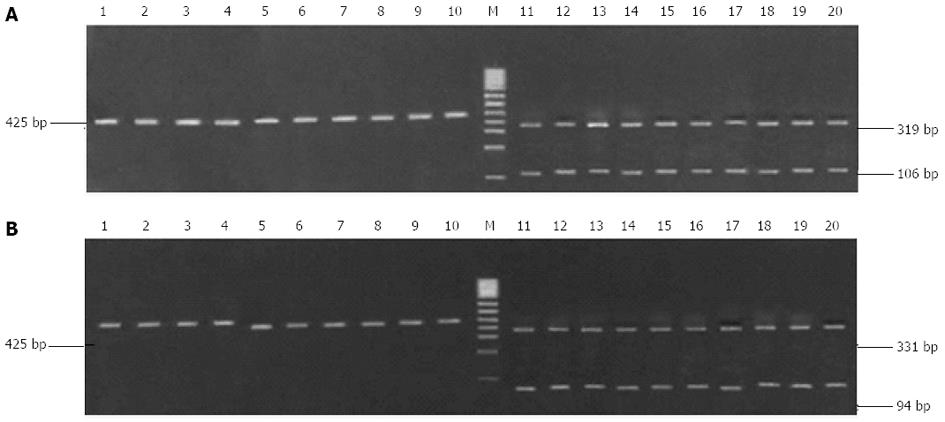
Figure 3 Digestion of the amplified fragment of the 23S rRNA gene from Helicobacter pylori isolates with restriction endonuclease Bbs I (A) and Bsa I (B).
1-10: Randomly selected clarithromycin-sensitive strains; 11-20: Randomly selected clarithromycin-resistant strains; M: 100 bp DNA ladder.
-
Citation: Zhao LJ, Huang YQ, Chen BP, Mo XQ, Huang ZS, Huang XF, Wei LD, Wei HY, Chen YH, Tang HY, Huang GR, Qin YC, Li XH, Wang LY.
Helicobacter pylori isolates from ethnic minority patients in Guangxi: Resistance rates, mechanisms, and genotype. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(16): 4761-4770 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i16/4761.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4761