Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2014; 20(16): 4692-4701
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4692
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4692
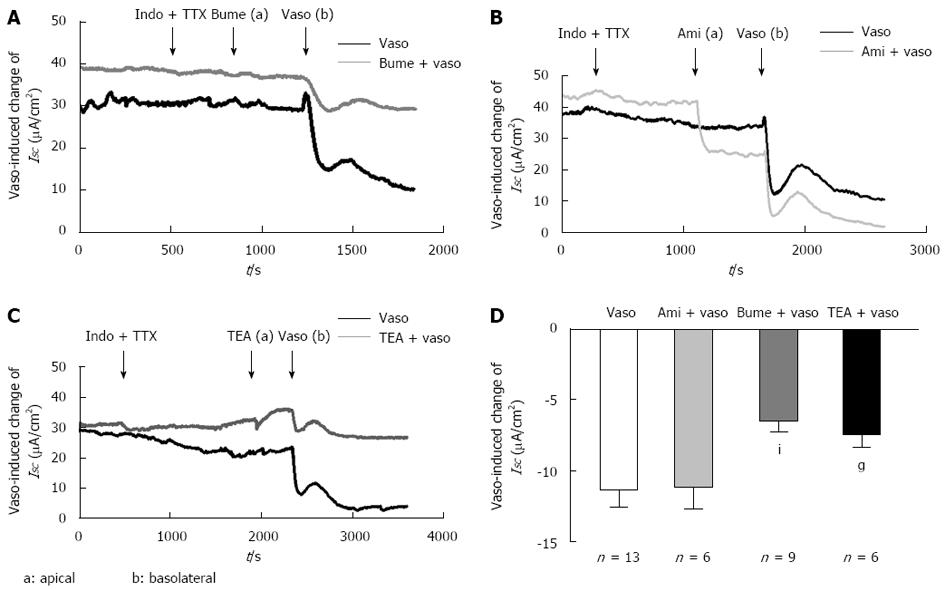
Figure 4 Apical Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter involvement in the serosal vasopressin-induced ISC response.
A: Representative ISC recordings in response to indomethacin (10 μmol, basolateral), TTX (tetrodotoxin, 1 μmol/L, basolateral), bumetanide (10 μmol/L, apical), and vasopressin (5 × 10-8 mol/L, basolateral); B: Representative ISC recordings in response to indomethacin (10 μmol/L, basolateral), TTX (tetrodotoxin, 1 μmol/L basolateral), amiloride (10 μmol/L, apical), and vasopressin (5 × 10-8 mol/L, basolateral). Arrows indicate the time of drug addiction; C: Representative ISC recordings in response to indomethacin (10 μmol/L, basolateral), TTX (tetrodotoxin, 1 μmol/L, basolateral), TEA (5 mmol/L, apical), and vasopressin (5 × 10-8 mol/L, basolateral); D: Comparison of the effects of serosal vasopressin on the ISC with or without apical pretreatment with bumetanide (n = 9), amiloride (n = 6) and TEA (n = 6). Values are mean ± SE; iP < 0.05; gP < 0.01.
- Citation: Xue H, Zhang ZJ, Li XS, Sun HM, Kang Q, Wu B, Wang YX, Zou WJ, Zhou DS. Localization and vasopressin regulation of the Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter in the distal colonic epithelium. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(16): 4692-4701
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i16/4692.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4692