Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2014; 20(16): 4662-4674
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4662
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4662
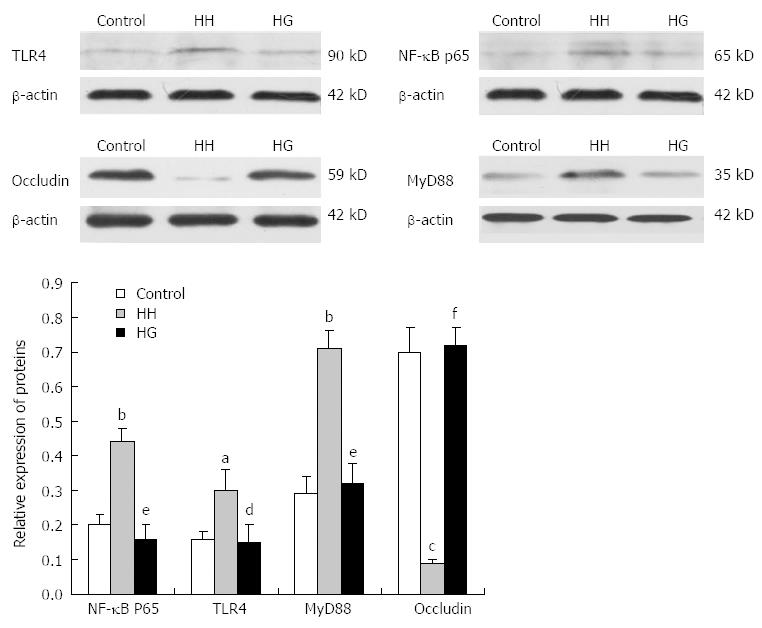
Figure 5 Toll-like receptor 4, nuclear factor-κB, myeloid differentiation factor 88, and occludin protein expression in the ileum of rats of different groups determined by Western blotting.
The occludin expression level in the HH group was lower than that in the Control group. After Gln treatment, the occludin expression level in the HG group was significantly higher than that in the HH group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs Control; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs HH. Values presented as means ± SEM (n = 4, each). Gln: Glutamine; Control: Control group; HH: Hypobaric hypoxia group; HG: Hypobaric hypoxia plus Gln group.
- Citation: Xu CL, Sun R, Qiao XJ, Xu CC, Shang XY, Niu WN. Protective effect of glutamine on intestinal injury and bacterial community in rats exposed to hypobaric hypoxia environment. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(16): 4662-4674
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i16/4662.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4662