Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2014; 20(16): 4662-4674
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4662
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4662
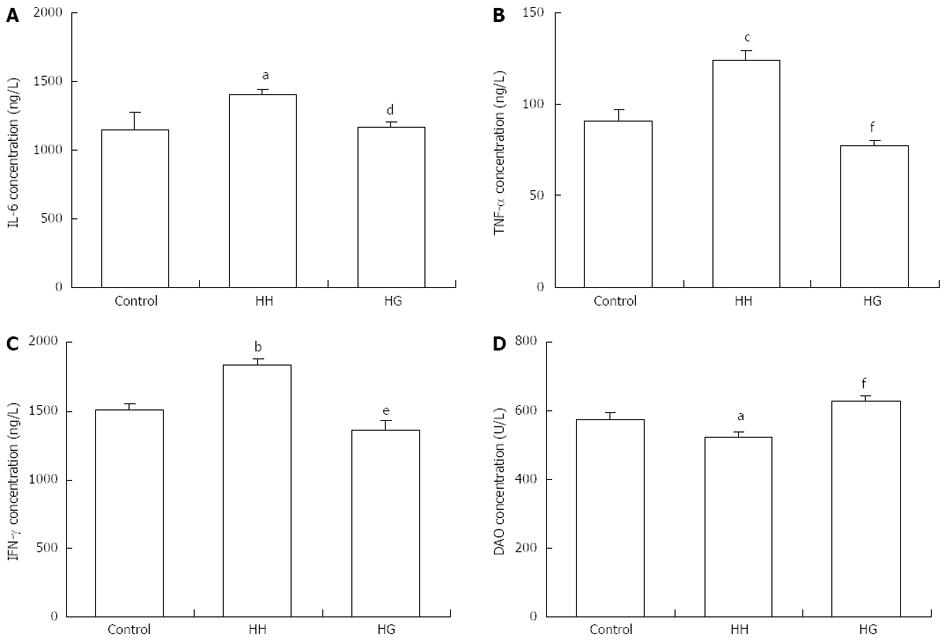
Figure 4 Effects of glutamine treatment on interleukin-6 (A), tumor necrosis factor-α (B), interferon-γ (C) and diamine oxidase contents in serum (D).
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs Control; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 vs HH. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 7, each). Gln: Glutamine; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; DAO: Diamine oxidase; Control: Control group; HH: Hypobaric hypoxia group; HG: Hypobaric hypoxia plus Gln treatment group.
- Citation: Xu CL, Sun R, Qiao XJ, Xu CC, Shang XY, Niu WN. Protective effect of glutamine on intestinal injury and bacterial community in rats exposed to hypobaric hypoxia environment. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(16): 4662-4674
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i16/4662.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4662