Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2014; 20(16): 4648-4661
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4648
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4648
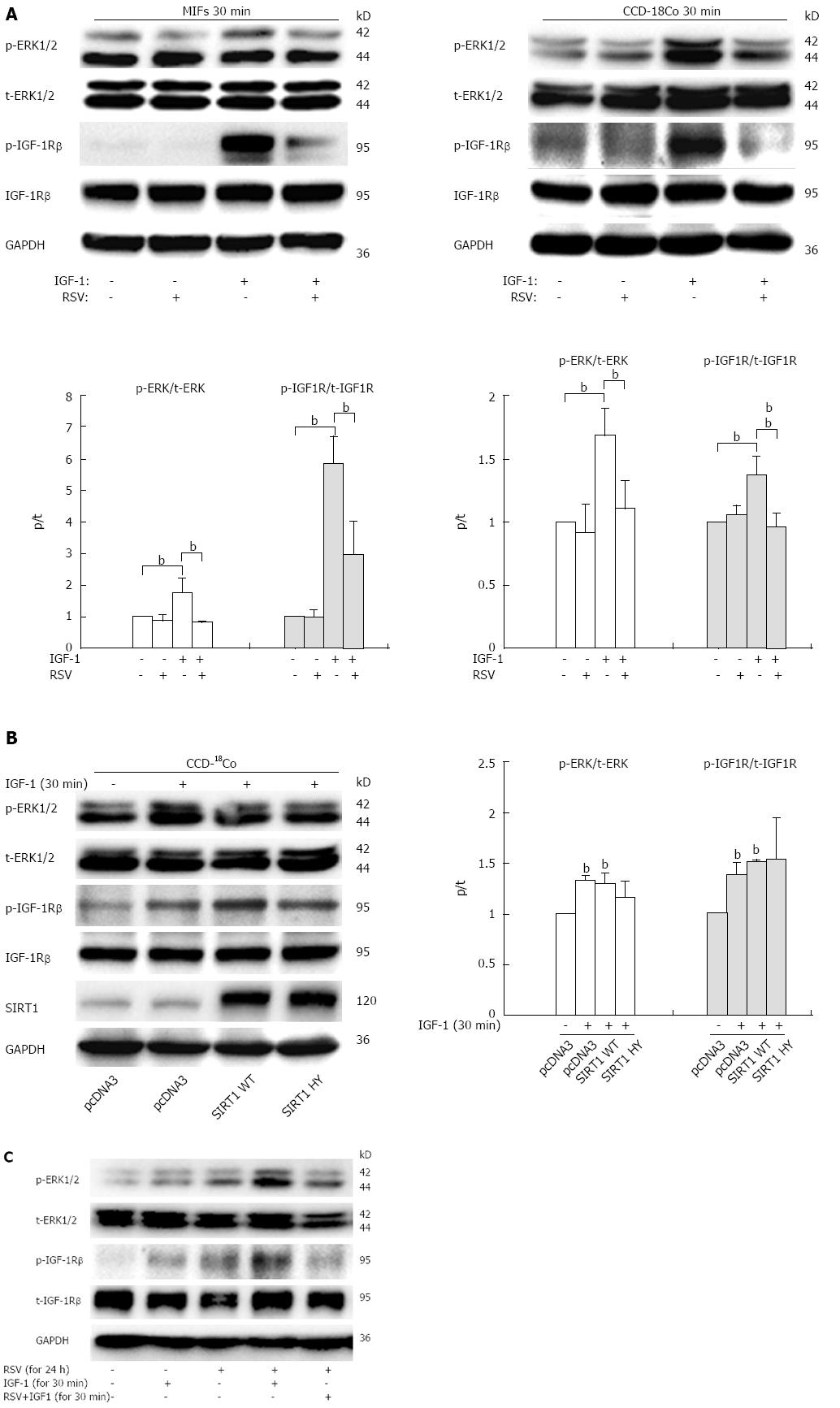
Figure 4 Resveratrol attenuates insulin growth factor-1 receptor and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation induced by insulin growth factor-1 via a silent information regulator 1-independent pathway.
A: Mouse intestinal fibroblasts (MIFs) and CCD-18Co cells were treated with 100 ng/mL insulin growth factor-1 (IGF-1) in the absence or presence of resveratrol (100 μmol/L) for 30 min; B: CCD-18Co cells were transfected with silent information regulator 1 (SIRT1) expression constructs [wild type SIRT1 (WT) or enzyme deficient SIRT1 (HY)] followed by exposure to 100 ng/mL IGF-1 for 30 min. The phosphorylated levels of IGF-1R and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 were measured; C: Serum-starved quiescent CCD-18Co cells were pretreated with 100 μmol/L of resveratrol for 24 h, then removed and stimulated with IGF-1 alone (column 4) or IGF-1 plus resveratrol (column 5) for 30 min. The bar graph represents the quantitation of the Western blotting normalized to the control. The experiment was repeated three times and obtained similar results. Values represent mean ± SD. bP < 0.01 vs control.
- Citation: Li P, Liang ML, Zhu Y, Gong YY, Wang Y, Heng D, Lin L. Resveratrol inhibits collagen I synthesis by suppressing IGF-1R activation in intestinal fibroblasts. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(16): 4648-4661
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i16/4648.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4648