Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2014; 20(16): 4636-4647
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4636
Published online Apr 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4636
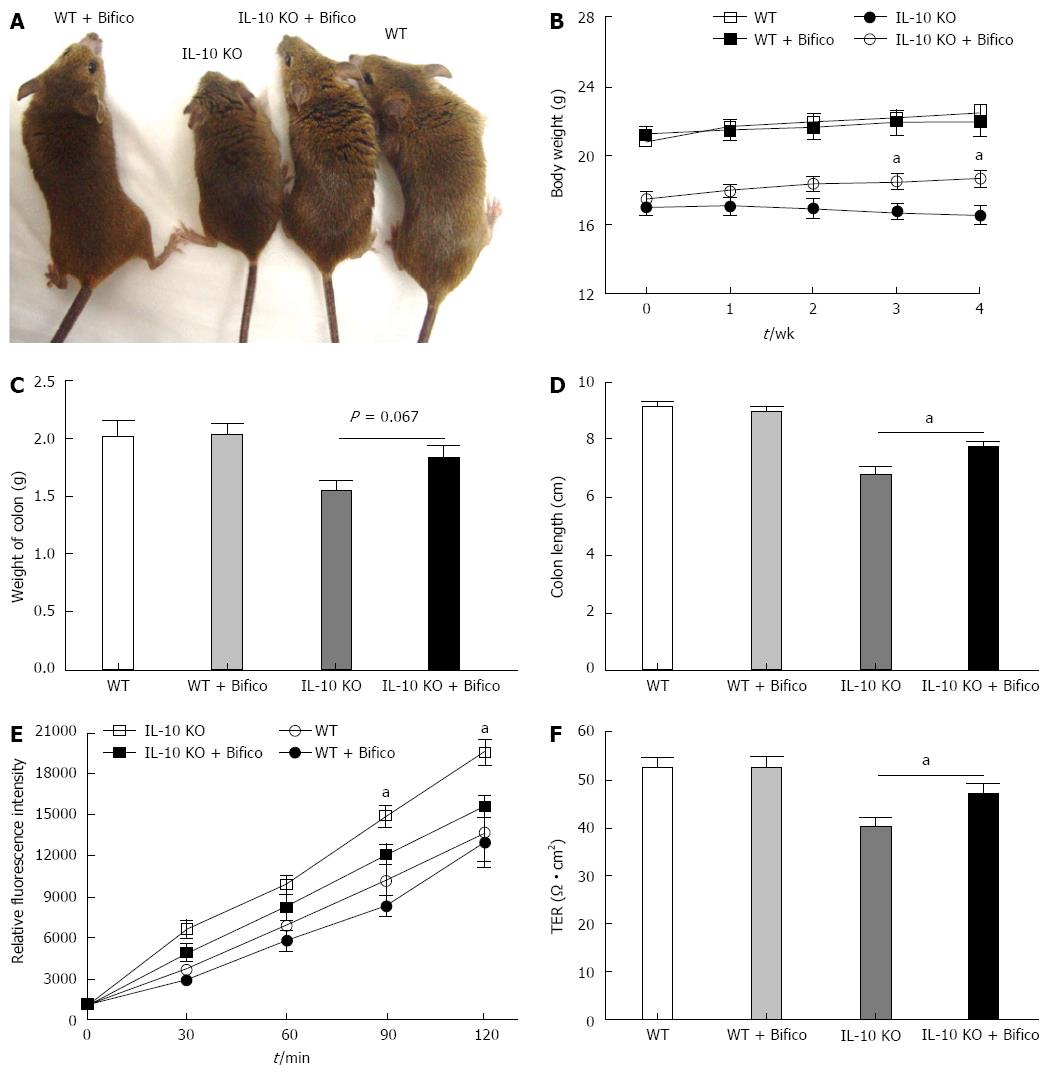
Figure 1 Bifico reduced clinical disease activity and prevented colonic epithelial permeability in interleukin-10 gene-deficient mice.
A: Representative photographs from the indicated mice for 4 wk following Bifico treatment; B: Changes in body weight. The IL-10 KO group was significantly lighter than the IL-10 KO + Bifico group (mean ± SEM, n = 6 per time point per group, aP < 0.05, Student’s t test); C: Colon weight were measured at 28 d following Bifico treatment; D: Colon length was measured at 28 d following Bifico treatment. IL-10 KO mice had shorter colons than IL-10 KO mice treated with Bifico. No difference in colon weight was observed (mean ± SEM, n = 6 per group, aP < 0.05, Student’s t test); E: Colonic paracellular permeability measured by cumulative permeability of nonabsorbable tracer molecule inulin-FITC; F: Colonic paracellular permeability measured by TER. IL-10 KO mice presented higher permeability than IL-10 KO mice treated with Bifico (mean ± SEM, n = 5 per time point per group, aP < 0.05, Student’s t test).
- Citation: Shi CZ, Chen HQ, Liang Y, Xia Y, Yang YZ, Yang J, Zhang JD, Wang SH, Liu J, Qin HL. Combined probiotic bacteria promotes intestinal epithelial barrier function in interleukin-10-gene-deficient mice. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(16): 4636-4647
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i16/4636.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i16.4636