Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2014; 20(15): 4316-4328
Published online Apr 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4316
Published online Apr 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4316
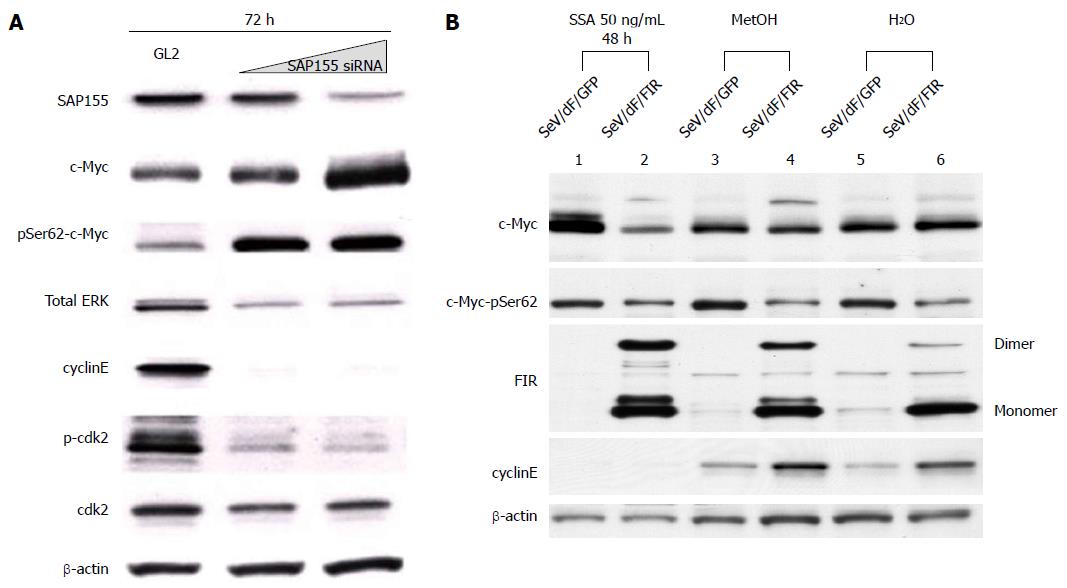
Figure 6 SAP155 siRNA induces c-Myc activation with ErK phosphorylation, but suppresses phosphorylated-cdk2/cyclinE expression.
HeLa cells were treated with SAP155 siRNA for three days (72 h). A: SAP155 siRNA, as well as SSA treatment, increased not only c-Myc expression level, but also c-Myc phosphorylation at both Ser62, but suppressed phosphorylated-cdk2 and cyclinE in a dose-dependent manner. Thus, SAP155 siRNA activates c-Myc potentially via inhibiting endogenous FIR pre-mRNA splicing; B: FIR Sendai virus (SeV/dF/FIR) reversed the cytotoxicity of SSA by suppressing activated endogenous c-Myc. HeLa cells were treated with 50 ng/mL SSA for 48 h with control (MetOH and H2O). 10 MOI of SeV/dF/FIR apparently suppressed activated c-Myc expression, whereas SeV/dF/FIR did not influence basal expression (MetOH or H2O). FIR: FBP Interacting Repressor; FBP: FUSE-Binding protein; FUSE: Far Upstream Element; SeV: Sendai virus; GFP: Green fluorescent protein; MOI: Multiplicity of infection; SSA: Spliceostatin.
-
Citation: Matsushita K, Shimada H, Ueda Y, Inoue M, Hasegawa M, Tomonaga T, Matsubara H, Nomura F. Non-transmissible Sendai virus vector encoding
c-myc suppressor FBP-interacting repressor for cancer therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(15): 4316-4328 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i15/4316.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4316