Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2014; 20(15): 4160-4166
Published online Apr 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4160
Published online Apr 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4160
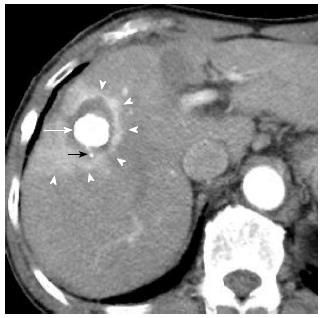
Figure 2 A 80-year-old woman with 2.
5 cm hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation combined with transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Early-phase dynamic computed tomography shows a high-density center indicating Lipiodol deposition in hepatocellular carcinoma (white arrow) and a surrounding low-density zone indicating radiofrequency ablation-induced coagulation necrosis of the liver. A microsatellite (black arrow) was depicted as a high-density spot in the low-density zone. Therefore, this ablation therapy achieved complete necrosis of chief tumor and micrometastasis. Moreover, hyperemia surrounding the ablated lesion is depicted as peripheral rim enhancement (arrowheads).
- Citation: Minami Y, Nishida N, Kudo M. Therapeutic response assessment of RFA for HCC: Contrast-enhanced US, CT and MRI. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(15): 4160-4166
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i15/4160.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4160