Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2014; 20(14): 4076-4084
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4076
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4076
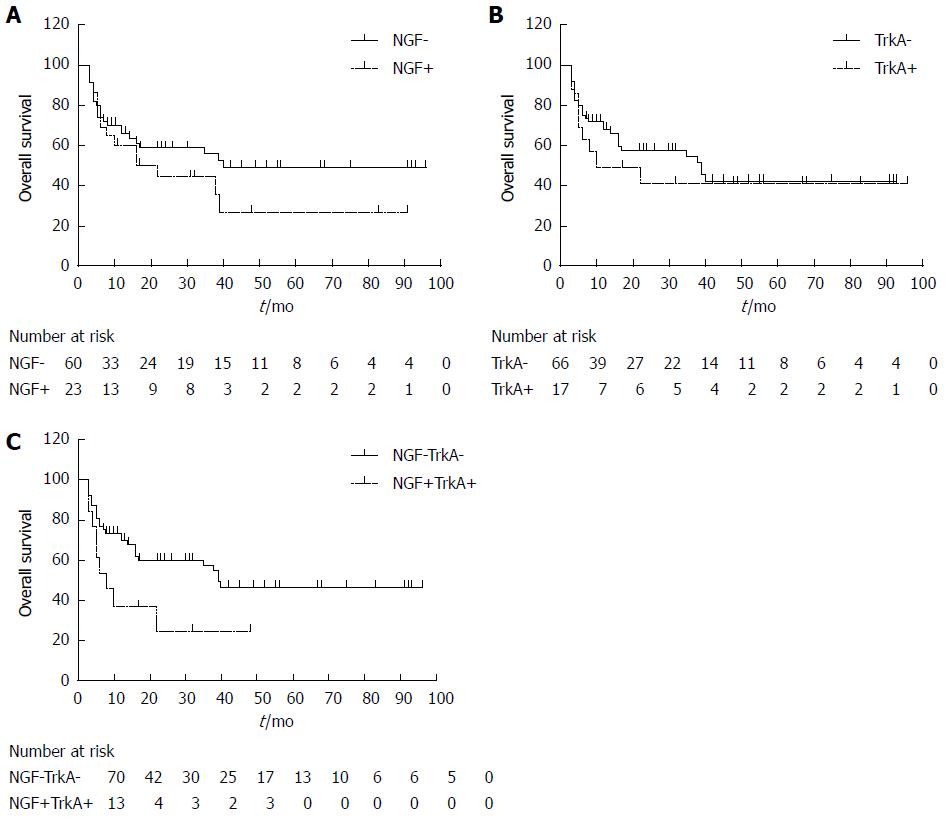
Figure 2 Correlations between overall survival rate and detected proteins.
Expressions of NGF (A) and TrkA (B) have no significant association with prognosis of IHCC (P = 0.201 and 0.483, respectively). The group with NGF and TrkA double higher expression had poorer prognosis than the non-NGF/TrkA double higher group (C) (including both lower expression, only NGF higher and only TrkA higher, P = 0.003). NGF: Nerve growth factor; IHCC: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma; TrkA: Tropomyosin-receptor-kinase.
- Citation: Yang XQ, Xu YF, Guo S, Liu Y, Ning SL, Lu XF, Yang H, Chen YX. Clinical significance of nerve growth factor and tropomyosin-receptor-kinase signaling pathway in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(14): 4076-4084
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i14/4076.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4076