Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2014; 20(14): 4050-4058
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4050
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4050
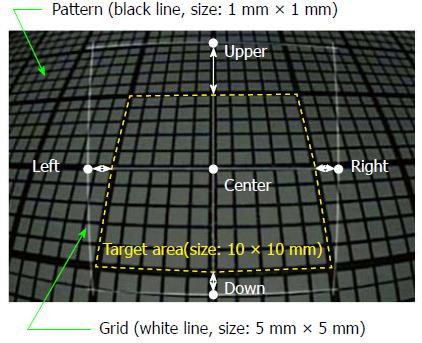
Figure 2 Endoscopic image with a 5 mm wide grid (distance between objects: 10 mm, tilt angle: 30°).
The pattern of a 1 mm square (black solid lines) was observed endoscopically (DBO: 10-40 mm, tilt angle: 0°-30°), and the 5 mm wide grid (white solid lines) was superimposed on the original image. The measurement errors (white arrows) were obtained by comparing the actual area (white dashed square line, size: 10 mm square) and four spots 5 mm away from the center of the grid (Upper, Lower, Right, Left). DBO: Distance between objects.
- Citation: Oka K, Seki T, Akatsu T, Wakabayashi T, Inui K, Yoshino J. Clinical study using novel endoscopic system for measuring size of gastrointestinal lesion. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(14): 4050-4058
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i14/4050.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.4050