Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2014; 20(14): 3916-3926
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3916
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3916
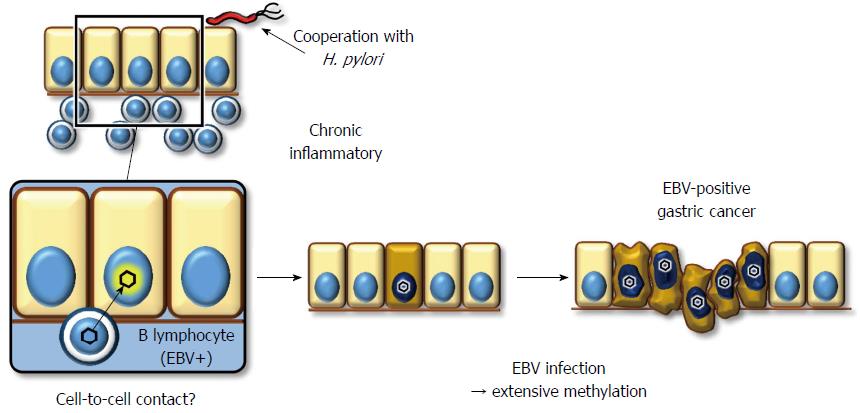
Figure 2 Schematic representation about infectious condition and pathogenicity of Epstein-Barr virus.
Direct cell-to-cell contact between B lymphocyte and gastric epithelial cell may perhaps be the most likely model to infect with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) into epithelial cells in vivo (left). EBV infection induces extensive promoter methylation, which should contribute to tumorigenesis. H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
-
Citation: Matsusaka K, Funata S, Fukayama M, Kaneda A. DNA methylation in gastric cancer, related to
Helicobacter pylori and Epstein-Barr virus. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(14): 3916-3926 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i14/3916.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3916