Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2014; 20(14): 3738-3750
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3738
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3738
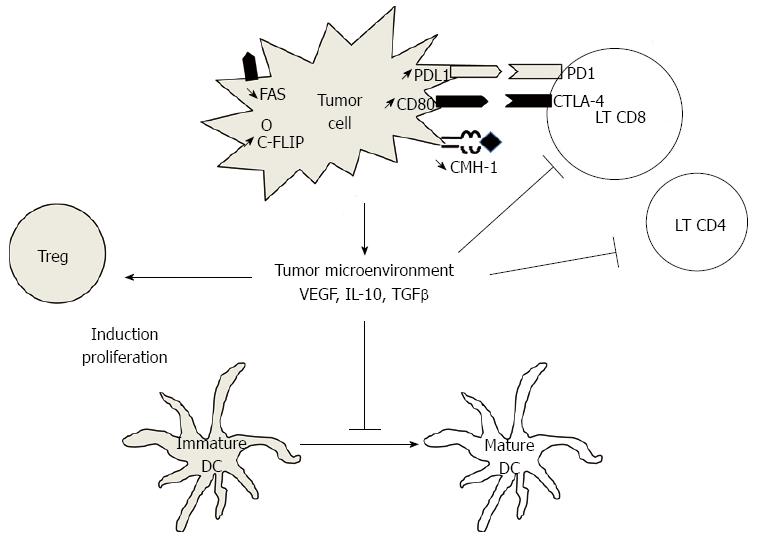
Figure 1 Major mechanisms of tumor immune escape.
Tumor cells can induce immunosuppression by different pathways: (1) tumor cells can secrete immunosuppressive cytokines as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), interleukin-10 (IL-10) or transforming growth factor-β (TGFβ). These molecules contribute to blockade of maturation of dendritic cells (DC) and then induce regulatory T cells (Treg) rather than lymphocytes T (LT) CD4+ or CD8+ cells. VEGF could promote directly induction and proliferation of Treg; (2) Tumor cells down-regulate expression of CMH-1; (3) Tumor cell express inhibitory molecules as PDL1 or CD80, and induce exhaustion of LT; and (4) Tumor cells can evade apoptosis by inducing anti-apoptotic molecules such as C-FLIP, or by down-regulating the expression of death receptors such as FAS.
- Citation: Pernot S, Terme M, Voron T, Colussi O, Marcheteau E, Tartour E, Taieb J. Colorectal cancer and immunity: What we know and perspectives. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(14): 3738-3750
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i14/3738.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3738