Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2014; 20(14): 3719-3737
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3719
Published online Apr 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3719
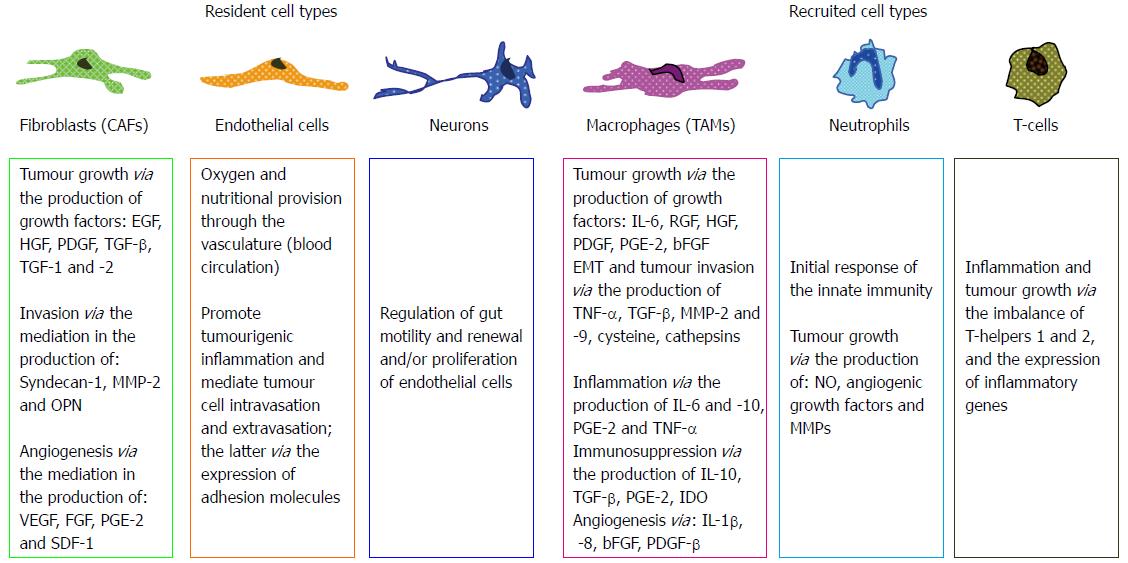
Figure 3 Various cellular types[22,23,112].
Various cellular types (resident: fibroblasts, endothelial cells and neurons, or recruited: macrophages, neutrophils and lymphocytes) which mediate cancer progression and growth in the colorectal microenvironment. bFGF: Basic fibroblast growth factor; CAF: Cancer associated fibroblasts; ECM: Extracellular matrix; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; EMT: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; IDO: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; IGF: Insulin growth factor; IL-10: Interleukin 10; MMP: Matrix metalloprotease; NO: Nitric oxide; OPN: Osteopontin; PDGF-β: Platelet-derived growth factor-beta; PGE2: Prostaglandin E2; SDF-1: Stromal cell-derived factor-1; TAM: Tumor-associated macrophages; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-beta; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor-alpha; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
- Citation: Paschos KA, Majeed AW, Bird NC. Natural history of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer - pathobiological pathways with clinical significance. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(14): 3719-3737
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i14/3719.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i14.3719