Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2014; 20(13): 3620-3627
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3620
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3620
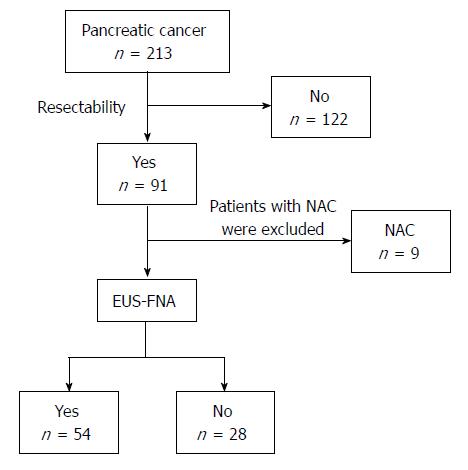
Figure 1 Study participants.
This flowchart explains how the final sample size was arrived at and which patients were included. Ninety-one patients with pancreatic cancer underwent radical surgery. Nine patients were treated with chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy preoperatively and were therefore excluded. The remaining 82 patients were divided into 2 groups. One group consisted of patients who underwent endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) before the operation (FNA+ group; n = 54), and the other group included patients who did not undergo EUS-FNA before the operation (FNA- group; n = 28). The decision to use preoperative EUS-FNA was made by a surgeon. NAC: Neoadjuvant chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy; EUS-FNA: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration.
- Citation: Kudo T, Kawakami H, Kuwatani M, Eto K, Kawahata S, Abe Y, Onodera M, Ehira N, Yamato H, Haba S, Kawakubo K, Sakamoto N. Influence of the safety and diagnostic accuracy of preoperative endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration for resectable pancreatic cancer on clinical performance. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(13): 3620-3627
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i13/3620.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3620