Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2014; 20(13): 3597-3608
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3597
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3597
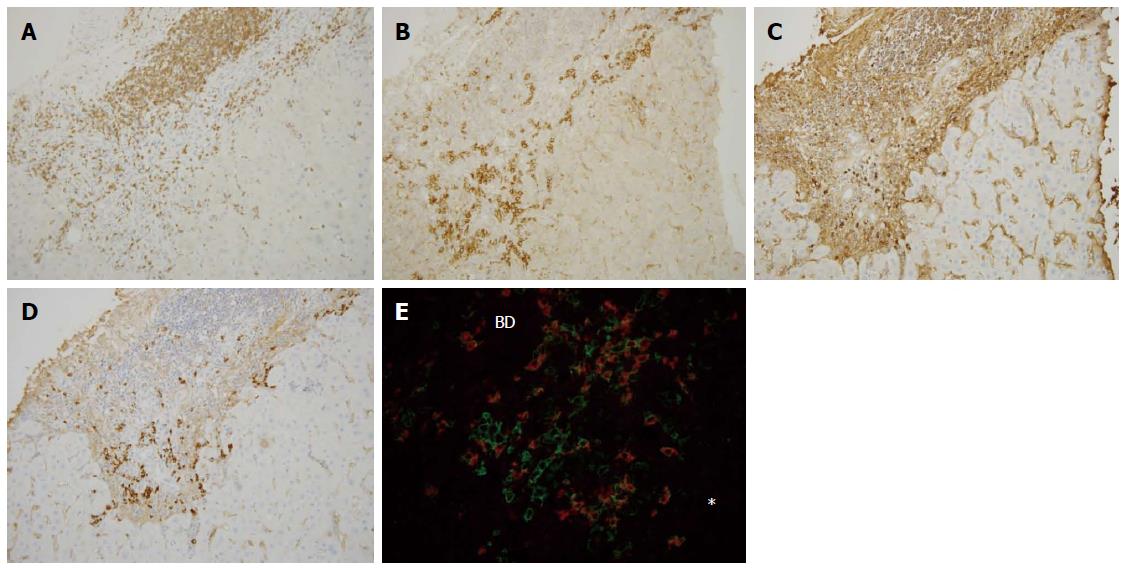
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical findings of primary biliary cirrhosis with interface hepatitis.
Many CD3+ cells were found within the portal tract and at the interface (A), whereas CD38+ cells heavily infiltrated the interface (B), IgG+ cells were mainly found in the portal tract and also at the interface (C), and IgM+ cell infiltration was predominant at the interface (D). Double staining for IgM (red) and CD38 (green) (E) showed that IgM-CD38 double positive cells, IgM-producing plasma cells, were frequently seen in the periportal area (star) (original magnifications: × 200). IgM+ plasma cells were also found around the intralobular bile duct. Asterisk: Hepatic lobule, BD: Bile duct.
- Citation: Kobayashi M, Kakuda Y, Harada K, Sato Y, Sasaki M, Ikeda H, Terada M, Mukai M, Kaneko S, Nakanuma Y. Clinicopathological study of primary biliary cirrhosis with interface hepatitis compared to autoimmune hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(13): 3597-3608
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i13/3597.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3597