Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2014; 20(13): 3582-3589
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3582
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3582
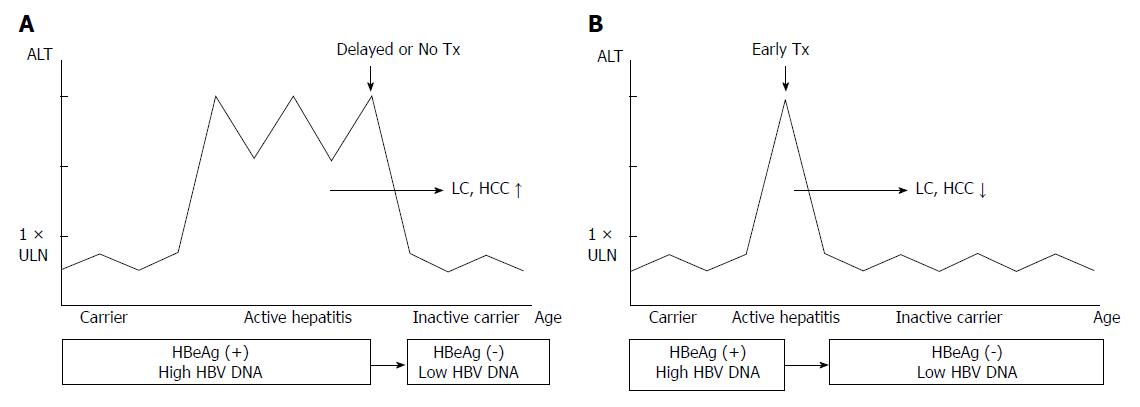
Figure 1 Altered course of chronic hepatitis B according to timing of starting treatment (Tx).
A: Delayed or no treatment results in higher incidence of liver cirrhosis (LC) or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); B: Treatment in early immune-clearance phase results in lower incidence of LC or HCC. ALT should be higher than 2 times of upper limit of normal values (> 2 × ULN); HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
- Citation: Choe HJ, Choe BH. What physicians should know about the management of chronic hepatitis B in children: East side story. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(13): 3582-3589
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i13/3582.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3582