Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2014; 20(13): 3443-3456
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3443
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3443
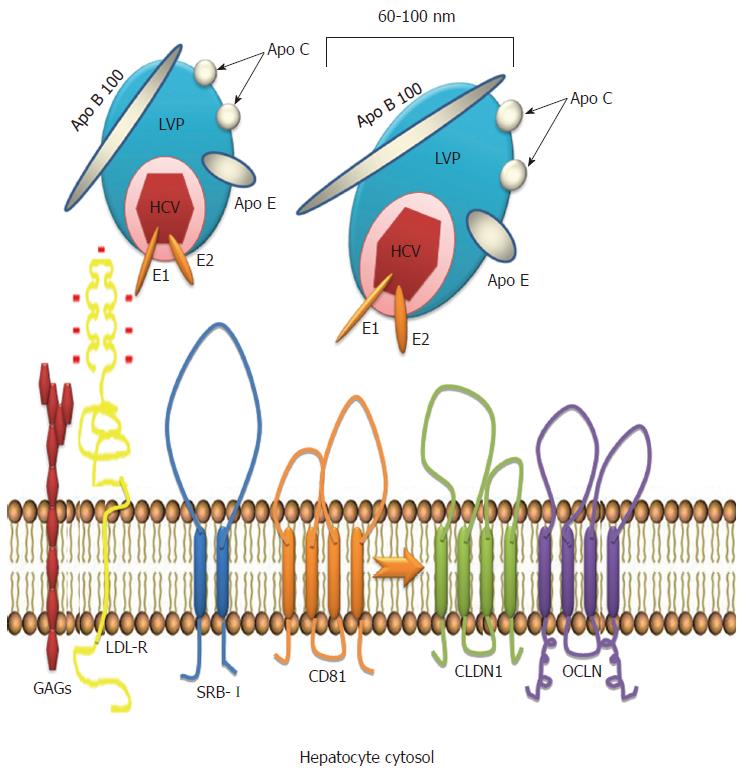
Figure 2 Hepatitis C virus entry.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) binds to lipoproteins and forms the lipo viro particle (LVP). LVP is attached by the hepatic low density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors through viral surface membrane proteins E1 and E2. After the initial phase, the LVP interacts with several input factors: the scavenger receptor class B type I (SRB-I), the membrane receptor CD81, coreceptors claudin 1 (CLDN1) and ocludin (OCLN). LVP is internalized into the cytosol by endocytosis.
- Citation: Fierro NA, Gonzalez-Aldaco K, Torres-Valadez R, Martinez-Lopez E, Roman S, Panduro A. Immunologic, metabolic and genetic factors in hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(13): 3443-3456
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i13/3443.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3443